Fabrication and Evaluation of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Corn Starch/Patchouli Oil Hydrogel Films Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized in Pogostemon cablin Benth Leaves' Extract
- PMID: 36903266
- PMCID: PMC10004108
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28052020
Fabrication and Evaluation of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Corn Starch/Patchouli Oil Hydrogel Films Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized in Pogostemon cablin Benth Leaves' Extract
Abstract
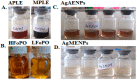
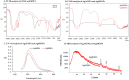
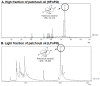
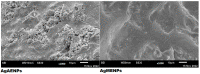
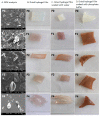
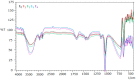
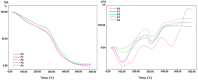
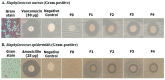
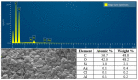
Research on the manufacture of hydrogel films from polyvinyl alcohol, corn starch, patchouli oil, and silver nanoparticles, (PVA/CS/PO/AgNPs, respectively) was completed. The silver nanoparticles used in this study resulted from green synthesis using local patchouli plants (Pogostemon cablin Benth). Aqueous patchouli leaf extract (APLE) and methanol patchouli leaf extract (MPLE) are used in the synthesis of phytochemicals (green synthesis), which are then blended in the production of PVA/CS/PO/AgNPs hydrogel films, which are then cross linked with glutaraldehyde. The results demonstrated that the hydrogel film was flexible, easy to fold, and free of holes and air bubbles. The presence of hydrogen bonds between the functional groups of PVA, CS, and PO was revealed using FTIR spectroscopy. SEM analysis revealed that the hydrogel film was slightly agglomerated and did not exhibit cracking or pinholes. The analysis of pH, spreadability, gel fraction, and swelling index showed that the resulting PVA/CS/PO/AgNP hydrogel films met expected standards except for the organoleptic properties of the resulting colors, which tended to be slightly darker in color. The formula with silver nanoparticles synthesized in methanolic of patchouli leaf extract (AgMENPs) had the highest thermal stability compared to hydrogel films with silver nanoparticles synthesized in aqueous of patchouli leaf extract (AgAENPs). The hydrogel films can be safely used up to 200 °C. The antibacterial studies revealed that the films inhibited the growth of both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermis, as determined by the disc diffusion method, with the best antibacterial activity being against Staphylococcus aureus. In conclusion, the hydrogel film F1, loaded with silver nanoparticles biosynthesized in aqueous of patchouli leave extract (AgAENPs) and light fraction of patchouli oil (LFoPO) performed the best activity against both Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermis.
Keywords: Pogostemon cablin Benth; Staphylococcus aureus; Staphylococcus epidermis; hydrogel films; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Posangi I., Posangi J., Wuisan J. Efek Ekstrak Daun Sirsak (Annona muricata L.) Pada Kadar Kolesterol Total Tikus Wistar. J. Biomedik JBM. 2012;4:37–42. doi: 10.35790/jbm.4.1.2012.750. - DOI
-
- Swamy M.K., Sinniah U.R. Patchouli (Pogostemon cablin Benth.): Botany, Agrotechnology and Biotechnological Aspects. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016;87:161–176. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.032. - DOI
-
- Ismalita, Khairan K., Rahmi, Muhammad S., Indra I. Green Synthesis of Sulfur Nanoparticles Using Allium sativum: Its Effects on the Growth of Pogostemon cablin Benth. and the Chemical Characterization of the Patchouli Oil after Being Harvested. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2022;7:359–375. doi: 10.1007/s41204-022-00217-5. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

