Diosmin and Bromelain Stimulate Glutathione and Total Thiols Production in Red Blood Cells
- PMID: 36903535
- PMCID: PMC10005239
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28052291
Diosmin and Bromelain Stimulate Glutathione and Total Thiols Production in Red Blood Cells
Abstract
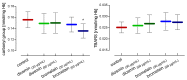
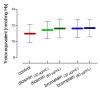
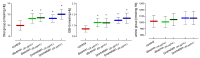
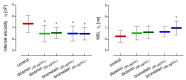
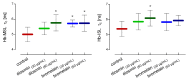
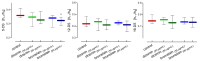
Diosmin and bromelain are bioactive compounds of plant origin with proven beneficial effects on the human cardiovascular system. We found that diosmin and bromelain slightly reduced total carbonyls levels and had no effect on TBARS levels, as well as slightly increased the total non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity in the RBCs at concentrations of 30 and 60 µg/mL. Diosmin and bromelain induced a significant increase in total thiols and glutathione in the RBCs. Examining the rheological properties of RBCs, we found that both compounds slightly reduce the internal viscosity of the RBCs. Using the MSL (maleimide spin label), we revealed that higher concentrations of bromelain led to a significant decrease in the mobility of this spin label attached to cytosolic thiols in the RBCs, as well as attached to hemoglobin at a higher concentration of diosmin, and for both concentrations of bromelain. Both compounds tended to decrease the cell membrane fluidity in the subsurface area, but not in the deeper regions. An increase in the glutathione concentration and the total level of thiol compounds promotes the protection of the RBCs against oxidative stress, suggesting that both compounds have a stabilizing effect on the cell membrane and improve the rheological properties of the RBCs.
Keywords: bromelain; diosmin; oxidative stress; red blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kilit A.C., Köse O., Imi G., Aydemir E. Research Article Anticancer and antimicrobial activities of diosmin. Genet. Mol. Res. 2021;20:gmr18752. doi: 10.4238/gmr18752. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

