Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Panax notoginseng Flower Saponins Quantified Using LC/MS/MS
- PMID: 36903661
- PMCID: PMC10005202
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28052416
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Panax notoginseng Flower Saponins Quantified Using LC/MS/MS
Abstract
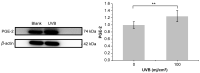
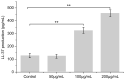
Panax notoginseng (Burk) F. H. Chen is a traditional Chinese medicinal and edible plant. However, Panax notoginseng flower (PNF) is rarely used. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to explore the main saponins and the anti-inflammatory bioactivity of PNF saponins (PNFS). We explored the regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), a key mediator of inflammatory pathways, in human keratinocyte cells treated with PNFS. A cell model of UVB-irradiation-induced inflammation was established to determine the influence of PNFS on inflammatory factors and their relationship with LL-37 expression. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting analysis were used to detect the production of inflammatory factors and LL37. Finally, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry was employed to quantify the main active components (ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc, Rd, Re, Rg1, and notoginsenoside R1) in PNF. The results show that PNFS substantially inhibited COX-2 activity and downregulated the production of inflammatory factors, indicating that they can be used to reduce skin inflammation. PNFS also increased the expression of LL-37. The contents of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc, and Rd in PNF were much higher than those of Rg1, and notoginsenoside R1. This paper provides data in support of the application of PNF in cosmetics.
Keywords: LC/MS/MS; Panax notoginseng flower; UVB; antibacterial peptide LL-37; inflammatory factor; total saponin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Liu Y.C., Zhang T.J., Guo H.B., Xu J., Lin J., Zhang H.B., Han Y.Q., Wang D.Q., Li C.Y., Liu C.X. Research progress and predictive analysis of quality markers of Panax notoginseng. Chin. Herbal Med. 2021;9:2733–2745. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.09.023. - DOI
-
- Gan C.M., Chen H.Y., Gong Y.Q. Notoginseng flower the research progress of chemical composition. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Yunnan. 2019;40:73–75. doi: 10.16254/j.carolcarrollnki.53-1120/r.2019.09.028. - DOI
-
- Peng X.X., Zhang S.H., Wang X.L., Ye T., Li H., Yan X., Wei X., Wu Z., Hu J., Zou C., et al. Panax Notoginseng flower saponins (PNFS) inhibit LPS-stimulated NO overproduction and iNOS gene overexpression via the suppression of TLR4-mediated MAPK/NF-kappa B signaling pathways in RAW264. 7 macrophages. Chin Med. 2015;10:15. doi: 10.1186/s13020-015-0045-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

