Ecotoxicological Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanomorphologies in Daphnia magna
- PMID: 36903805
- PMCID: PMC10005163
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13050927
Ecotoxicological Properties of Titanium Dioxide Nanomorphologies in Daphnia magna
Abstract
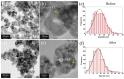
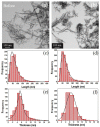
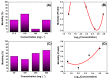
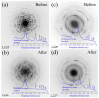
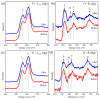
In this work, the structural, vibrational, morphological, and colloidal properties of commercial 15.1 nm TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) and nanowires (NWs, 5.6 thickness, 74.6 nm length) were studied with the purpose of determining their ecotoxicological properties. This was achieved by evaluating acute ecotoxicity experiments carried out in the environmental bioindicator Daphnia magna, where their 24-h lethal concentration (LC50) and morphological changes were evaluated using a TiO2 suspension (pH = 7) with point of zero charge at 6.5 for TiO2 NPs (hydrodynamic diameter of 130 nm) and 5.3 for TiO2 NWs (hydrodynamic diameter of 118 nm). Their LC50 values were 157 and 166 mg L-1 for TiO2 NWs and TiO2 NPs, respectively. The reproduction rate of D. magna after fifteen days of exposure to TiO2 nanomorphologies was delayed (0 pups for TiO2 NWs and 45 neonates for TiO2 NPs) in comparison with the negative control (104 pups). From the morphological experiments, we may conclude that the harmful effects of TiO2 NWs are more severe than those of 100% anatase TiO2 NPs, likely associated with brookite (36.5 wt. %) and protonic trititanate (63.5 wt. %) presented in TiO2 NWs according to Rietveld quantitative phase analysis. Specifically, significant change in the heart morphological parameter was observed. In addition, the structural and morphological properties of TiO2 nanomorphologies were investigated using X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy techniques to confirm the physicochemical properties after the ecotoxicological experiments. The results reveal that no alteration in the chemical structure, size (16.5 nm for TiO2 NPs and 6.6 thickness and 79.2 nm length for NWs), and composition occurred. Hence, both TiO2 samples can be stored and reused for future environmental purposes, e.g., water nanoremediation.
Keywords: aquatic biota; biomarkers; metal-oxides; nanoparticles; nanowires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Kumar J.A., Krithiga T., Manigandan S., Sathish S., Renita A.A., Prakash P., Prasad B.S.N., Kumar T.R.P., Rajasimman M., Hosseini-Bandegharaei A., et al. A focus to green synthesis of metal/metal-based oxide nanoparticles: Various mechanisms and applications towards ecological approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;324:129198. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129198. - DOI
-
- Chouke P.B., Shrirame T., Potbhare A.K., Mondal A., Chaudhary A.R., Mondal S., Thakare S.R., Nepovimova E., Valis M., Kuca K., et al. Bioinspired metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A road map to potential applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2022;16:100314. doi: 10.1016/j.mtadv.2022.100314. - DOI
-
- Abdallah A.M., Abdel-Rahman A.A., Elwardany A.E. Analysis of the impact of different nanoparticle metal oxides as fuel additives in compression ignition engine performance. Energy Rep. 2020;6:99–105. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2020.12.016. - DOI
-
- Ağbulut Ü., Karagöz M., Sarıdemir S., Öztürk A. Impact of various metal-oxide based nanoparticles and biodiesel blends on the combustion, performance, emission, vibration and noise characteristics of a CI engine. Fuel. 2020;270:117521. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117521. - DOI
-
- Faraji J., Sepehri A., Salcedo-Reyes J.C. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles and Sodium Nitroprusside Alleviate the Adverse Effects of Cadmium Stress on Germination and Seedling Growth of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Univ. Sci. 2018;23:61–87. doi: 10.11144/Javeriana.SC23-1.tdna. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

