Antiphotoaging and Skin-Protective Activities of Ardisia silvestris Ethanol Extract in Human Keratinocytes
- PMID: 36904025
- PMCID: PMC10007040
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12051167
Antiphotoaging and Skin-Protective Activities of Ardisia silvestris Ethanol Extract in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
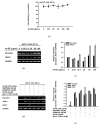
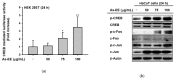
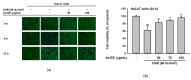
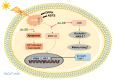
Ardisia silvestris is a traditional medicinal herb used in Vietnam and several other countries. However, the skin-protective properties of A. silvestris ethanol extract (As-EE) have not been evaluated. Human keratinocytes form the outermost barrier of the skin and are the main target of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. UV exposure causes skin photoaging via the production of reactive oxygen species. Protection from photoaging is thus a key component of dermatological and cosmetic products. In this research, we found that As-EE can prevent UV-induced skin aging and cell death as well as enhance the barrier effect of the skin. First, the radical-scavenging ability of As-EE was checked using DPPH, ABTS, TPC, CUPRAC, and FRAP assays, and a 3-(4-5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2-5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay was used to examine cytotoxicity. Reporter gene assays were used to determine the doses that affect skin-barrier-related genes. A luciferase assay was used to identify possible transcription factors. The anti-photoaging mechanism of As-EE was investigated by determining correlated signaling pathways using immunoblotting analyses. As-EE had no harmful effects on HaCaT cells, according to our findings, and As-EE revealed moderate radical-scavenging ability. With high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, rutin was found to be one of the major components. In addition, As-EE enhanced the expression levels of hyaluronic acid synthase-1 and occludin in HaCaT cells. Moreover, As-EE dose-dependently up-regulated the production of occludin and transglutaminase-1 after suppression caused by UVB blocking the activator protein-1 signaling pathway, in particular, the extracellular response kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Our findings suggest that As-EE may have anti-photoaging effects by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase, which is good news for the cosmetics and dermatology sectors.
Keywords: AP-1; Ardisia silvestris ethanol extract; ROS; UVB irradiation; anti-apoptosis; antioxidative capacity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Anti-photoaging activities of Sorbaria kirilowii ethanol extract in UVB-damaged cells.Cytotechnology. 2021 Feb;73(1):127-138. doi: 10.1007/s10616-020-00449-w. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Cytotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33505120 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Photoaging Effect of Phaseolus angularis L. Extract on UVB-Exposed HaCaT Keratinocytes and Possibilities as Cosmetic Materials.Molecules. 2023 Feb 1;28(3):1407. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031407. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771069 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Quercus acuta Thunb. fruit extract against UVB-induced photoaging through ERK/AP-1 signaling modulation in human keratinocytes.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 4;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03473-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 34983480 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Potentilla glabra in UVB-Induced Photoaging Process.Molecules. 2021 Sep 6;26(17):5408. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175408. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500840 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Wrinkling and Anti-Melanogenic Effect of Pradosia mutisii Methanol Extract.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 27;20(5):1043. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051043. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30818884 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Composition and Skin-Friendly Activities of the Ethyl Acetate Fraction in Ophioglossum vulgatum Linn., an In Vitro Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;18(3):345. doi: 10.3390/ph18030345. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143123 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

