Mechanisms of Foreign Body Giant Cell Formation in Response to Implantable Biomaterials
- PMID: 36904554
- PMCID: PMC10007405
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15051313
Mechanisms of Foreign Body Giant Cell Formation in Response to Implantable Biomaterials
Abstract
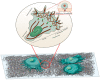
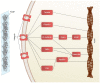
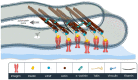
Long term function of implantable biomaterials are determined by their integration with the host's body. Immune reactions against these implants could impair the function and integration of the implants. Some biomaterial-based implants lead to macrophage fusion and the formation of multinucleated giant cells, also known as foreign body giant cells (FBGCs). FBGCs may compromise the biomaterial performance and may lead to implant rejection and adverse events in some cases. Despite their critical role in response to implants, there is a limited understanding of cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in forming FBGCs. Here, we focused on better understanding the steps and mechanisms triggering macrophage fusion and FBGCs formation, specifically in response to biomaterials. These steps included macrophage adhesion to the biomaterial surface, fusion competency, mechanosensing and mechanotransduction-mediated migration, and the final fusion. We also described some of the key biomarkers and biomolecules involved in these steps. Understanding these steps on a molecular level would lead to enhance biomaterials design and improve their function in the context of cell transplantation, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
Keywords: actin cytoskeleton; biomaterials; foreign body giant cells (FBGCs); immune response; macrophages fusion; mechanotransduction.
Conflict of interest statement
M. R.M. is in the scientific advisory board of XOStem Inc. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mohammadi M., Luong J.C., Rodriguez S.M., Cao R., Wheeler A.E., Lau H., Li S., Shabestari S.K., Chadarevian J.P., Alexander M., et al. Controlled release of stem cell secretome attenuates inflammatory response against implanted biomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020;9:1901874. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901874. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mohammadi M.R., Rodrigez S., Cao R., Alexander M., Lakey J.R.T. Immune response to subcutaneous implants of alginate microcapsules. Mater. Today Proc. 2018;5:15580–15585. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.04.166. - DOI
-
- Eslami-kaliji F., Sarafbidabad M., Kiani-Esfahani A., Mirahmadi-Zare S.Z., Dormiani K. 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid a bio-immunomodulator in tissue engineering; generates tolerogenic dendritic cells by blocking the toll-like receptor 4. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A. 2021;2021 109:1575–1587. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37152. - DOI - PubMed

