Efficacy of detergent-based cleaning and wiping against SARS-CoV-2 on high-touch surfaces
- PMID: 36906280
- PMCID: PMC11417498
- DOI: 10.1093/lambio/ovad033
Efficacy of detergent-based cleaning and wiping against SARS-CoV-2 on high-touch surfaces
Abstract
Efficacy of cleaning methods against SARS-CoV-2 suspended in either 5% soil load (SARS-soil) or simulated saliva (SARS-SS) was evaluated immediately (hydrated virus, T0) or 2 hours post-contamination (dried virus, T2). Hard water dampened wiping (DW) of surfaces, resulted in 1.77-3.91 log reduction (T0) or 0.93-2.41 log reduction (T2). Incorporating surface pre-wetting by spraying with a detergent solution (D + DW) or hard water (W + DW) just prior to dampened wiping did not unilaterally increase efficacy against infectious SARS-CoV-2, however, the effect was nuanced with respect to surface, viral matrix, and time. Cleaning efficacy on porous surfaces (seat fabric, SF) was low. W + DW on stainless steel (SS) was as effective as D + DW for all conditions except SARS-soil at T2 on SS. DW was the only method that consistently resulted in > 3-log reduction of hydrated (T0) SARS-CoV-2 on SS and ABS plastic. These results suggest that wiping with a hard water dampened wipe can reduce infectious virus on hard non-porous surfaces. Pre-wetting surfaces with surfactants did not significantly increase efficacy for the conditions tested. Surface material, presence or absence of pre-wetting, and time post-contamination affect efficacy of cleaning methods.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; cleaning; coronavirus; disinfection; high-touch surfaces; surfactant; virucide; virus.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Applied Microbiology International 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest statement
Neither Battelle nor the EPA manufacture or provide the products or materials described herein, nor plan to manufacture or provide these products in the future. No conflicts of interest declared.
Figures
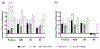

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

