Neutralizing activity and 3-month durability of tixagevimab and cilgavimab prophylaxis against Omicron sublineages in transplant recipients
- PMID: 36906295
- PMCID: PMC9835002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajt.2022.11.002
Neutralizing activity and 3-month durability of tixagevimab and cilgavimab prophylaxis against Omicron sublineages in transplant recipients
Abstract
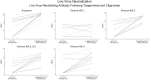
Neutralizing antibody (nAb) responses are attenuated in solid organ transplant recipients (SOTRs) despite severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 vaccination. Preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with the antibody combination tixagevimab and cilgavimab (T+C) might augment immunoprotection, yet in vitro activity and durability against Omicron sublineages BA.4/5 in fully vaccinated SOTRs have not been delineated. Vaccinated SOTRs, who received 300 + 300 mg T+C (ie, full dose), within a prospective observational cohort submitted pre and postinjection samples between January 31, 2022, and July 6, 2022. The peak live virus nAb was measured against Omicron sublineages (BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1, and BA.4), and surrogate neutralization (percent inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor binding to full length spike, validated vs live virus) was measured out to 3 months against sublineages, including BA.4/5. With live virus testing, the proportion of SOTRs with any nAb increased against BA.2 (47%-100%; P < .01), BA.2.12.1 (27%-80%; P < .01), and BA.4 (27%-93%; P < .01), but not against BA.1 (40%-33%; P = .6). The proportion of SOTRs with surrogate neutralizing inhibition against BA.5, however, fell to 15% by 3 months. Two participants developed mild severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 infection during follow-up. The majority of fully vaccinated SOTRs receiving T+C PrEP achieved BA.4/5 neutralization, yet nAb activity commonly waned by 3 months postinjection. It is critical to assess the optimal dose and interval of T+C PrEP to maximize protection in a changing variant climate.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron variant; cilgavimab; monoclonal antibody; organ transplant; tixagevimab.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

