This is a preprint.
Rolosense: Mechanical detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a DNA-based motor
- PMID: 36909543
- PMCID: PMC10002644
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.02.27.530294
Rolosense: Mechanical detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a DNA-based motor
Update in
-
Rolosense: Mechanical Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using a DNA-Based Motor.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 May 21;10(7):1332-1347. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00312. eCollection 2024 Jul 24. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071064 Free PMC article.
Abstract
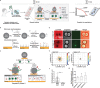
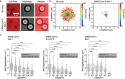
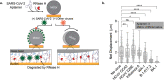
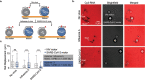
Assays detecting viral infections play a significant role in limiting the spread of diseases such as SARS-CoV-2. Here we present Rolosense, a virus sensing platform that transduces the motion of synthetic DNA-based motors transporting 5-micron particles on RNA fuel chips. Motors and chips are modified with virus-binding aptamers that lead to stalling of motion. Therefore, motors perform a "mechanical test" of viral target and stall in the presence of whole virions which represents a unique mechanism of transduction distinct from conventional assays. Rolosense can detect SARS-CoV-2 spiked in artificial saliva and exhaled breath condensate with a sensitivity of 103 copies/mL and discriminates among other respiratory viruses. The assay is modular and amenable to multiplexing, as we demonstrated one-pot detection of influenza A and SARS-CoV-2. As a proof-of-concept, we show readout can be achieved using a smartphone camera in as little as 15 mins without any sample preparation steps. Taken together, mechanical detection using Rolosense can be broadly applied to any viral target and has the potential to enable rapid, low-cost, point-of-care screening of circulating viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rolosense: Mechanical Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using a DNA-Based Motor.ACS Cent Sci. 2024 May 21;10(7):1332-1347. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00312. eCollection 2024 Jul 24. ACS Cent Sci. 2024. PMID: 39071064 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of a Smartphone-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Viruses.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jan 4;5(1):e2145669. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.45669. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35089353 Free PMC article.
-
A mask-based diagnostic platform for point-of-care screening of Covid-19.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Nov 15;192:113486. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113486. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 34260968 Free PMC article.
-
Review of non-invasive detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens in exhaled breath condensate.J Breath Res. 2022 Mar 18;16(2):10.1088/1752-7163/ac59c7. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/ac59c7. J Breath Res. 2022. PMID: 35235925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-based Emerging Tools for Viral Biomarker Detection: A Focus on SARS-CoV-2.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(8):910-934. doi: 10.2174/1568009622666220214101059. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35156569 Review.
References
-
- Nawattanapaiboon K. et al. Colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) as a visual diagnostic platform for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. The Analyst 146, 471–477 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
