Houston Methodist Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Guidelines
- PMID: 36910549
- PMCID: PMC10000315
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcvj.1177
Houston Methodist Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Guidelines
Abstract
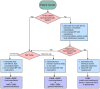
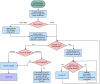
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (RAAA) is an acute aortic condition that requires emergent intervention and appropriate continuity of care to optimize patient outcomes. We describe the standardized RAAA protocol at the Houston Methodist Hospital Acute Aortic Treatment Center, developed to navigate critical patient transfer periods safely and efficiently, make crucial decisions about surgical intervention, and clearly communicate these plans with other care team providers. Our workflow is organized into five phases: prehospital, preoperative, intraoperative, postoperative, and post-discharge. We identify the transfer center, anesthesia, operating room nursing staff, surgeons, and intensive care unit as key entities of our acute aortic pathology care team. This systematic protocol for the management of acute aortic emergencies such as RAAA identifies critical decision points, potential complications at each stage, and recommendations for best practice.
Keywords: RAAA Timeout; THROMBINS2; acute aortic syndromes; guidelines; patient outcomes; protocol; ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm; transfer of care.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- YouTube.com [Internet]. San Bruno, CA: YouTube; c2022. Atkins M, Rahimi M, Bavare C. Current management of ruptured AAA; 2021. Feb 1 [cited 2023 Jan 27]. Available from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CpayxrjWm0k/
-
- Starnes BW, Mehta M, Veith FJ. Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: The Definitive Manual. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2017. 408 p. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-23844-9 - DOI
-
- Raux M, Marzelle J, Kobeiter H, et al. Endovascular balloon occlusion is associated with reduced intraoperative mortality of unstable patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm but fails to improve other outcomes. J Vasc Surg. 2015. Feb;61(2):304-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.07.098 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

