Branched and Fenestrated Aortic Endovascular Grafts
- PMID: 36910555
- PMCID: PMC10000330
- DOI: 10.14797/mdcvj.1200
Branched and Fenestrated Aortic Endovascular Grafts
Abstract
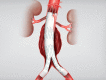
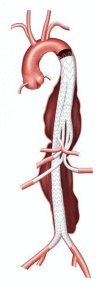
Endovascular repair of abdominal and descending thoracic aortic aneurysms has become the standard of care due to improvements in morbidity and mortality compared to open surgical repair. Late durability, however, remains an issue because persistent endoleaks can lead to continued aneurysm expansion and eventual rupture, sometimes years following the original repair. Branched, fenestrated, and physician-modified endografts in the thoracic arch and thoracoabdominal aorta have extended the seal zone in order to mitigate the risks of proximal and distal endoleaks. This review summarizes the current state of branched, fenestrated, and physician-modified endografts used in complex aortic pathologies.
Keywords: branched endograft; complex abdominal aortic aneurysm; fenestrated endograft; physician modified endograft; thoracic aortic aneurysm; thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm.
Copyright: © 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures




References
-
- CookMedical.com [Internet]. Bloomington, IN: Cook Medical; c2023. Zenith® Fenestrated AAA Endovascular Graft - Annual Clinical Update; 2019. (cited 2023 Feb 6]. Available from: https://www.cookmedical.com/data/resources/2019_Clinical-Update-for-Zeni...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

