Longitudinal phenotypic aging metrics in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging
- PMID: 36910594
- PMCID: PMC9997119
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-022-00243-7
Longitudinal phenotypic aging metrics in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging
Abstract
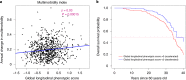
To define metrics of phenotypic aging, it is essential to identify biological and environmental factors that influence the pace of aging. Previous attempts to develop aging metrics were hampered by cross-sectional designs and/or focused on younger populations. In the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA), we collected longitudinally across the adult age range a comprehensive list of phenotypes within four domains (body composition, energetics, homeostatic mechanisms and neurodegeneration/neuroplasticity) and functional outcomes. We integrated individual deviations from population trajectories into a global longitudinal phenotypic metric of aging and demonstrate that accelerated longitudinal phenotypic aging is associated with faster physical and cognitive decline, faster accumulation of multimorbidity and shorter survival. These associations are more robust compared with the use of phenotypic and epigenetic measurements at a single time point. Estimation of these metrics required repeated measures of multiple phenotypes over time but may uniquely facilitate the identification of mechanisms driving phenotypic aging and subsequent age-related functional decline.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests M.E.L. holds licenses for epigenetic clocks that she has developed. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

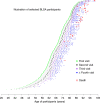
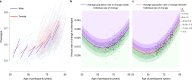

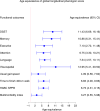
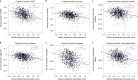

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG068285/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG028747/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG069915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000015/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG068673/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048069/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057912/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG070178/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000015/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG057545/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032947/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065403/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 AG999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

