Application of the PHENotype SIMulator for rapid identification of potential candidates in effective COVID-19 drug repurposing
- PMID: 36911878
- PMCID: PMC9986505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14115
Application of the PHENotype SIMulator for rapid identification of potential candidates in effective COVID-19 drug repurposing
Abstract
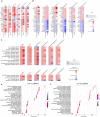
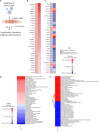
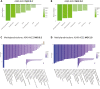
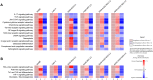
The current, rapidly diversifying pandemic has accelerated the need for efficient and effective identification of potential drug candidates for COVID-19. Knowledge on host-immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, however, remains limited with few drugs approved to date. Viable strategies and tools are rapidly arising to address this, especially with repurposing of existing drugs offering significant promise. Here we introduce a systems biology tool, the PHENotype SIMulator, which -by leveraging available transcriptomic and proteomic databases-allows modeling of SARS-CoV-2 infection in host cells in silico to i) determine with high sensitivity and specificity (both>96%) the viral effects on cellular host-immune response, resulting in specific cellular SARS-CoV-2 signatures and ii) utilize these cell-specific signatures to identify promising repurposable therapeutics. Powered by this tool, coupled with domain expertise, we identify several potential COVID-19 drugs including methylprednisolone and metformin, and further discern key cellular SARS-CoV-2-affected pathways as potential druggable targets in COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Keywords: 2DG, 2-Deoxy-Glucose; ACE2, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19; COVID-19, Coronavirus disease 2019; Caco-2, Human colon epithelial carcinoma cell line; Calu-3, Epithelial cell line; Cellular SARS-CoV-2 signatures; Cellular host-immune response; Cellular simulation models; DEGs, Differentially Expressed Genes; DEPs, Differentially expressed proteins; Drug repurposing; HCQ-CQ, (Hydroxy)chloroquine; IFN, Interferon; ISGs, IFN-stimulated genes; MITHrIL, Mirna enrIched paTHway Impact anaLysis; MOI, Multiplicity of infection; MP, Methylprednisolone; NHBE, Normal human bronchial epithelial cells; PHENSIM, PHENotype SIMulator; SARS-CoV-2, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Systems biology; TLR, Toll-like Receptor.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Rapid Identification of Druggable Targets and the Power of the PHENotype SIMulator for Effective Drug Repurposing in COVID-19.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Apr 14:rs.3.rs-287183. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-287183/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Heliyon. 2023 Mar;9(3):e14115. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14115. PMID: 33880466 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

