Estimating the effect of active detection and isolation on Clostridioides difficile infections in a bone marrow transplant unit
- PMID: 36912338
- PMCID: PMC10587385
- DOI: 10.1017/ice.2023.37
Estimating the effect of active detection and isolation on Clostridioides difficile infections in a bone marrow transplant unit
Abstract
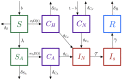
Objective: To model the effects of active detection and isolation (ADI) regarding Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) in the bone marrow transplant (BMT) unit of our hospital.
Setting: ADI was implemented in a 21-patient bone marrow unit.
Patients: Patients were bone marrow recipients on this unit.
Interventions: We compared active ADI, in which patients who tested positive for colonization of C. difficile before their hospital stay were placed under extra contact precautions, with cases not under ADI.
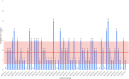
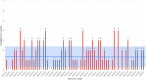
Results: Within the BMT unit, ADI reduced total cases of CDI by 24.5% per year and reduced hospital-acquired cases by ∼84%. The results from our simulations also suggest that ADI can save ∼$67,600 per year in healthcare costs.
Conclusions: Institutions with active BMT units should consider implementing ADI.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflicts of interest relevant to this article.
Figures


References
-
- CDC museum COVID-19 timeline. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html. Accessed August 2021.
-
- Spanos, CP. Clostridioides difficile colitis. In: Acute Surg Topics. New York: Springer Cham; 2021:65–69.
-
- Zimlichman E, Henderson D, Tamir O, et al. Healthcare-associated infections: a meta-analysis of costs and financial impact on the US healthcare system. JAMA Intern Med 2013;173:2039–2046. - PubMed
-
- Ofori E, Ramai D, Dhawan M, Mustafa F, Gasperino J, Reddy M. Community-acquired Clostridium difficile: epidemiology, ribotype, risk factors, hospital and intensive care unit outcomes, and current and emerging therapies. J Hosp Infect 2018;99:436–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

