Safety of Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- PMID: 36913180
- PMCID: PMC10010235
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-023-01840-5
Safety of Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Abstract
In recent years, better knowledge of the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) has led to a relevant expansion of the therapeutic arsenal for these conditions. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a family of small molecules that block one or more of the intracellular tyrosine kinases, including JAK-1, JAK-2, JAK-3 and TYK-2. Tofacitinib, a non-selective small molecule JAK inhibitor, and upadacitinib and filgotinib, which are selective JAK-1 inhibitors, have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for moderate-to-severe active ulcerative colitis. Compared to biological drugs, JAK inhibitors have a short half-life, rapid onset of action, and no immunogenicity. Both clinical trials and real-world evidence support the use of JAK inhibitors in the treatment of IBD. However, these therapies have been linked with multiple adverse events (AEs) including infection, hypercholesterolemia, venous thromboembolism, major adverse cardiovascular events, and malignancy. While early studies recognized several potential AEs, post-marketing trials have shown that tofacitinib may increase the risk of thromboembolic diseases and major cardiovascular events. The latter are seen in patients aged 50 years or older with cardiovascular risk factors. Hence, the benefits of treatment and risk stratification need to be considered when positioning tofacitinib. Novel JAK inhibitors with a more selective effect on JAK-1 have proven to be effective in both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, offering a potentially safer and efficacious therapeutic option to patients, including those with previous non-response to other therapies such as biologics. Nevertheless, long-term effectiveness and safety data are required.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PN has been a consultant for Janssen and Ferring, RQ has been a consultant for Jansen and AJY has been a consultant for Takeda, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Arena pharmaceuticals, Prometheus Labs and Procise.
Figures
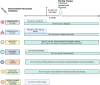
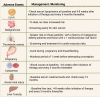
References
-
- Gilardi D, Gabbiadini R, Alloca M, Correale C, Fiorino G, Furfaro F, et al. PK, PD and interactions: the new scenario with JAK inhibitors and S1P receptor modulators, two classes of small molecules drugs in IBD. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14(9):797–806. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1785868. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

