Situation-Aware BDI Reasoning to Detect Early Symptoms of Covid 19 Using Smartwatch
- PMID: 36913222
- PMCID: PMC9983688
- DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3156819
Situation-Aware BDI Reasoning to Detect Early Symptoms of Covid 19 Using Smartwatch
Abstract
Ambient intelligence plays a crucial role in healthcare situations. It provides a certain way to deal with emergencies to provide the essential resources such as nearest hospitals and emergency stations promptly to avoid deaths. Since the outbreak of Covid-19, several artificial intelligence techniques have been used. However, situation awareness is a key aspect to handling any pandemic situation. The situation-awareness approach gives patients a routine life where they are continuously monitored by caregivers through wearable sensors and alert the practitioners in case of any patient emergency. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a situation-aware mechanism to detect Covid-19 systems early and alert the user to be self-aware regarding the situation to take precautions if the situation seems unlikely to be normal. We provide Belief-Desire-Intention intelligent reasoning mechanism for the system to analyze the situation after acquiring the data from the wearable sensors and alert the user according to their environment. We use the case study for further demonstration of our proposed framework. We model the proposed system by temporal logic and map the system illustration into a simulation tool called NetLogo to determine the results of the proposed system.
Keywords: Covid-19; NetLogo; Situation-awareness; ambient intelligence; belief-desire-intention (BDI); healthcare.
Figures






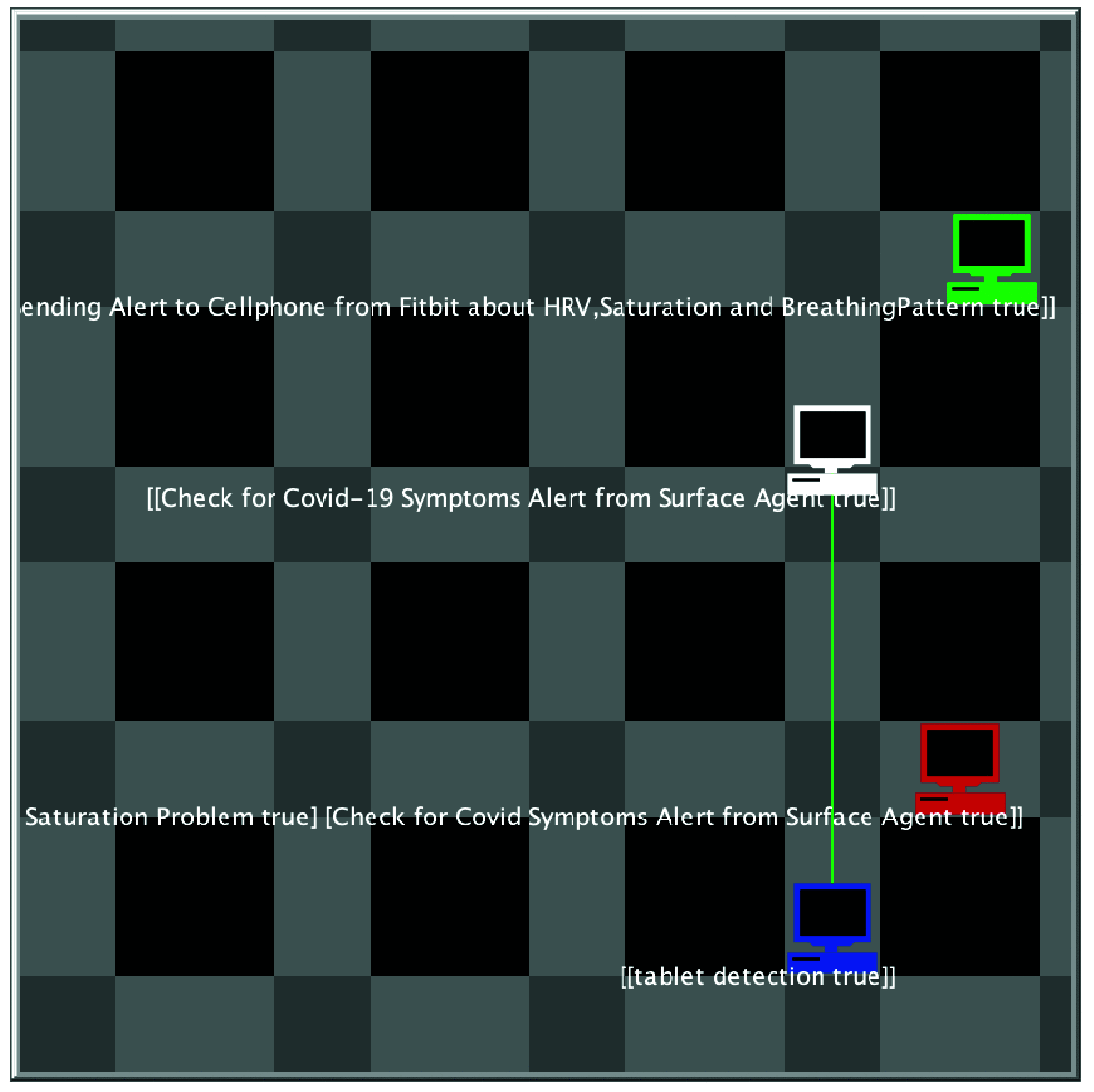

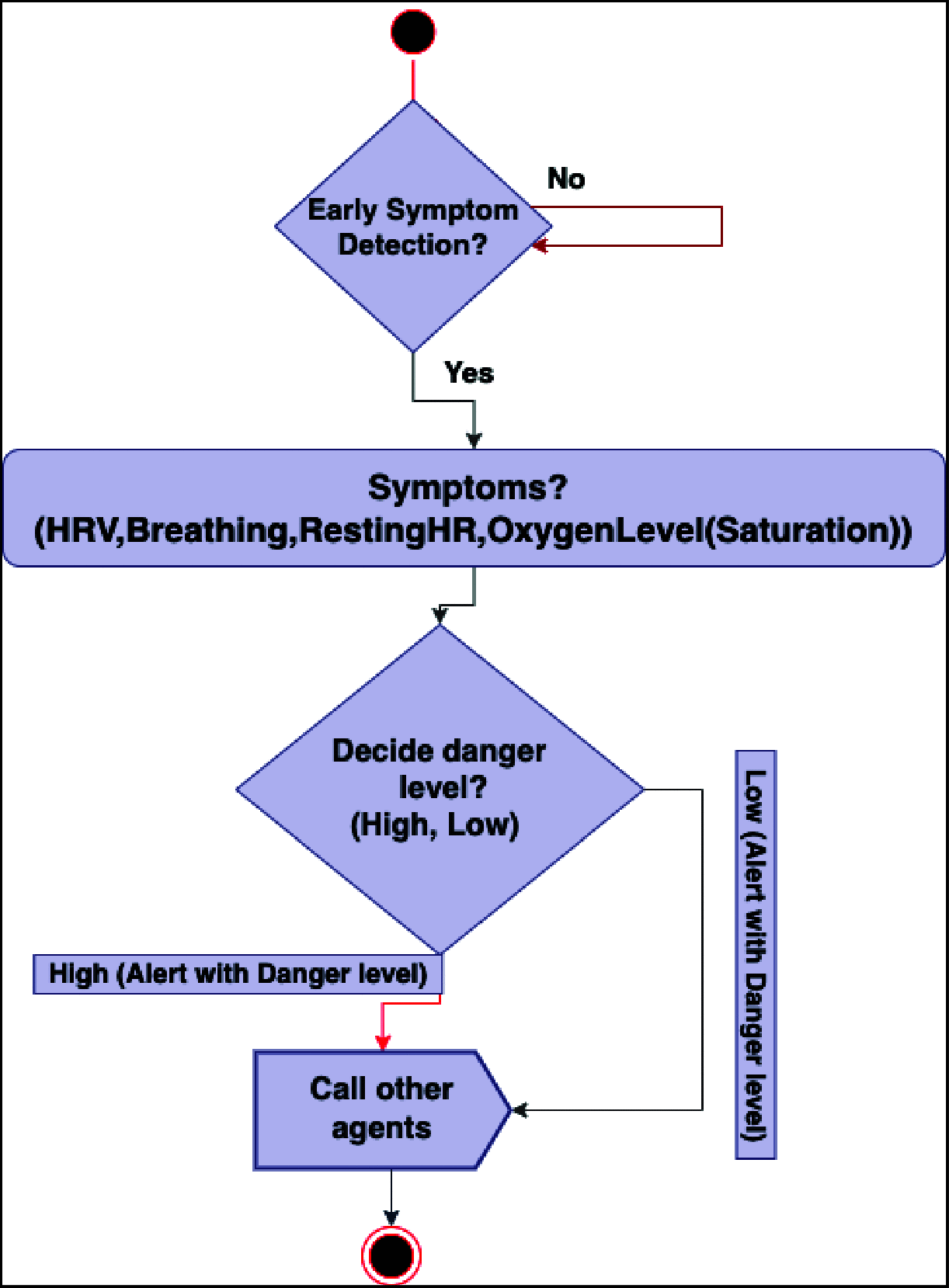

References
-
- Ayoub A.et al. , “Classification and categorization of COVID-19 outbreak in Pakistan,” Comput., Mater. Continua, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 1253–1269, 2021.
-
- Manoj M., Srivastava G., Somayaji S. R. K., Gadekallu T. R., Maddikunta P. K. R., and Bhattacharya S., “An incentive based approach for COVID-19 planning using blockchain technology,” in Proc. IEEE Globecom Workshops, Dec. 2020, pp. 1–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
