The approaching pilot for One Health governance index
- PMID: 36915165
- PMCID: PMC10009848
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-023-01067-2
The approaching pilot for One Health governance index
Abstract
Background: One Health approach advocates realizing the best health and harmonious symbiosis of human, animal and natural environment through cross-border, multi-sectoral and interdisciplinary cooperation. The good governance model is the leading factor for the performance of One Health governance. In order to tackle the complex problems in the One Health governance at the global level, the variation of One Health governance in different countries was analyzed by a set of indicators within the One Health system.
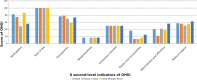
Method: The capacity of One Health governance was assessed after establishment of a set of indicators for the One Health governance index (OHGI) following the methodology of the global One Health index. The data to calculate OHGI was collected from various database sources, including the Food and Agriculture Organization, the World Health Organization, the World Organization for Animal Health, and official health-related institutions of various countries. Eight indicators (including 19 sub-indicators) were employed in the OHGI system to comprehensively evaluate the capacity of One Health governance in 146 countries of the world.
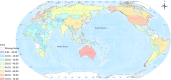
Results: Among the 146 countries scored in the OHGI system, the average score was 34.11, with a median score of 31.49, ranged from 8.50 to 70.28. Most countries with higher OHGI scores come from Europe and Central Asia, East Asia and the Pacific and North America, while countries with the lower OHGI scores are almost from sub-Saharan Africa. Six countries scored more than 65 points, including Australia, Sweden, Germany, Netherlands, the United States of America and Finland, indicating that these countries are relatively mature in most aspects of One Health governance. However, there were some developing countries with OHGI scored lower than 15. Therefore, the gap between countries with higher OHGI scores and those with lower OHGI scores is more than 60.
Conclusions: Good governance on One Health is an important indicator to measure One Health's governance capacity. The political stability, the level of rule of law and economic conditions in different regions are significantly correlated with the One Health governance capacity. Actions need to be taken urgently to close the gap of One Health governance between different regions.
Keywords: Developed countries; Developing countries; Governance; One Health; Rule of law.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Academician Chen Guoqiang (In China): the research on "One Health" is at the right time. https://www.cn-healthcare.com/article/20200317/content-532725.html. Accessed 21 Sept 2022.
-
- Food Safety Focus. https://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/multimedia/multimedia_pub/multimedia_pub_.... Accessed 21 Sept 2022.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

