Lifestyle, clinical, and occupational risk factors of recurrent stroke among the working-age group: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36915512
- PMCID: PMC10006477
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13949
Lifestyle, clinical, and occupational risk factors of recurrent stroke among the working-age group: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Stroke recurrence is increasing in the working-age population. This study aimed to summarize and evaluate the risk factors for recurrent stroke among the working-age population.
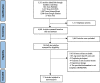
Methods: Relevant studies were extracted from several databases following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. Fixed- or random-effects estimates of the pooled odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of risk factors for recurrent stroke were generated based on heterogeneity. Subgroup and publication bias analyses were also performed.
Results: Seventeen studies were included in the meta-analysis. Pooled effects results revealed that the risk of recurrent stroke in the working-age group was as follows: Diabetes (OR = 1.85, 95% CI: 1.47, 2.32), hypertension (OR = 1.27, 95% CI: 1.12, 1.44), smoking (OR = 1.52, 95% CI: 1.27, 1.81), history of cardiac disease (OR = 2.86, 95% CI: 2.22, 3.67), history of stroke (OR = 2.45, 95% CI: 1.81, 3.31), and National Institutes of Health stroke severity score (OR = 1.09, 95% CI: 1.03, 1.15).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that several factors, such as diabetes, hypertension, smoking, history of cardiac disease and stroke, and severity of a stroke, are potential risk factors for recurrent stroke in the working-age group. Therefore, strategies to reduce those risk factors should be adopted and attention paid to prevent recurrent stroke among working-age populations.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Recurrent stroke; Risk factors; Working-age group.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- WHO The Top 10 Causes of Death. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death Available from.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

