The EGFR C797S Mutation Confers Resistance to a Novel EGFR Inhibitor CLN-081 to EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
- PMID: 36915628
- PMCID: PMC10006853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2023.100462
The EGFR C797S Mutation Confers Resistance to a Novel EGFR Inhibitor CLN-081 to EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
Abstract
Introduction: EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations account for 5% to 10% of EGFR-mutated NSCLC. CLN-081 (formerly known as TAS6417), a novel covalent EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, exhibits pan-mutation selective efficacy, including exon 20 insertions, in the clinical setting. Nevertheless, some patients may not respond to CLN-081 and resistance to CLN-081 may emerge over time in others.
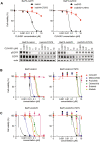
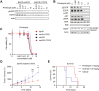
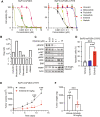
Methods: We exposed Ba/F3 cells transduced with EGFR exon 20 insertions (Y764_V765 insHH or A767_S768insSVD) to increasing concentrations of CLN-081 to generate resistant cells and then subjected their complementary DNA to sequencing to identify acquired mutations. We then evaluated effects of small molecules on engineered Ba/F3 cells on the basis of proliferation assays, Western blotting, and xenograft models.
Results: All CLN-081 resistant clones harbored the EGFR C797S mutation. Ba/F3 cells with C797S (Ba/F3-C797S) were resistant to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations, including CLN-081. Pimitespib, a selective heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, induced apoptosis in Ba/F3-C797S cells in vitro and inhibited growth of Ba/F3-C797S tumors in vivo. Ba/F3 cells with A763_Y764insFQEA-C797S remained sensitive to erlotinib.
Conclusions: We conclude that the EGFR C797S mutation confers resistance to CLN-081. Our preclinical data suggest a potential small molecule to overcome CLN-081 resistance, which may benefit patients with lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertions.
Keywords: C797S; CLN-081; EGFR; Non–small cell lung cancer; Resistant mechanism.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Zhou C., Wu Y.L., Chen G., et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Sequist L.v., Yang J.C.H., Yamamoto N., et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3327–3334. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y.L., Cheng Y., Zhou X., et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1454–1466. - PubMed
-
- Soria J.-C., Ohe Y., Vansteenkiste J., et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:113–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

