Immunophenotypic profiles and prognosis for colorectal mucinous adenocarcinomas are dependent on anatomic location
- PMID: 36916704
- PMCID: PMC10166970
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5803
Immunophenotypic profiles and prognosis for colorectal mucinous adenocarcinomas are dependent on anatomic location
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of mucinous adenocarcinomas (MCAs, exhibiting >50% extracellular mucin) of the colorectum, in relation to their anatomic location is not well studied.
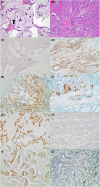
Materials and methods: We compared MCAs (n = 175) with non-MCAs (NMCAs, n = 1015) and the cancer-specific survival rates were evaluated, based on their anatomic site, by univariate Kaplan-Meier and multivariate Cox methods. Subsets of these tumors were immunostained for MUC1, MUC2, Bcl-2, and p53.
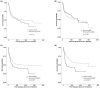
Results: MCAs were more commonly found in the right colon, were of high-grade, and were more prevalent in younger patients (<40 years). They exhibited strong expression of MUC2 and Bcl-2 and showed less p53 nuclear staining. In contrast, most NMCAs were low-grade with high expression of MUC1. MCAs of the rectum were associated with poorer outcomes relative to NMCAs (HR 1.85, CI 95% 1.15-2.97), even though the distributions of advanced-stage tumors were similar.
Conclusion: Late-stage disease and age were poor independent prognostic indicators of cancer-specific deaths across all tumor locations. In summary, rectal MCAs have a poor prognosis.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; mucinous adenocarcinomas; non-mucinous adenocarcinomas; prognostic biomarker; rectal cancers; tumor location.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hugen N, Brown G, Glynne‐Jones R, de Wilt JH, Nagtegaal ID. Advances in the care of patients with mucinous colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13(6):361‐369. - PubMed
-
- Ott C, Gerken M, Hirsch D, et al. Advanced mucinous colorectal cancer: epidemiology, prognosis and efficacy of chemotherapeutic treatment. Digestion. 2018;98(3):143‐152. - PubMed
-
- Catalano V, Loupakis F, Graziano F, et al. Prognosis of mucinous histology for patients with radically resected stage II and III colon cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):135‐141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

