Does anterior plus posterior interosseus neurectomy lead to better outcomes than isolated posterior interosseus denervation in the treatment of chronic wrist pain? A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36916712
- PMCID: PMC10026062
- DOI: 10.1530/EOR-22-0089
Does anterior plus posterior interosseus neurectomy lead to better outcomes than isolated posterior interosseus denervation in the treatment of chronic wrist pain? A systematic review of the literature and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Partial wrist denervation can be performed by isolated posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) or combined PIN plus (+) anterior interosseous nerve (AIN) neurectomy procedures. The purpose of the current systematic review is to investigate any differences in clinical outcomes and failures in patients undergoing AIN + PIN vs isolated PIN neurectomy.
Methods: A review of the English Literature was performed on Medline, WOS and Scopus according to PRISMA protocol combining 'wrist denervation', 'PIN neurectomy', 'AIN neurectomy', anterior interosseous nerve neurectomy' and 'posterior interosseous nerve neurectomy'. Studies were assessed with a modified Coleman Methodology Score (CMS). The primary outcome for meta-analysis was 'Failures', including all patients who have required a second surgery or those who are left with pain (defined as 'bad').
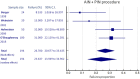
Results: Overall, 10 studies totalling 347 wrists were included in this systematic review, with a 'moderate' CMS. The isolated PIN neurectomy technique showed a 15.1% pooled failure rate at a median follow-up of 22 months, while the combined AIN+PIN denervation had a pooled failure rate of 23.6% at a follow-up with a median of 29 months. The combined analysis of both procedures did not show significantly better results in favour of either technique, with a general failure rate of 21.6% (P = 0.0501).
Conclusion: Partial denervation for chronic wrist pain is a salvage procedure that leads to an overall success of 78.4% for pain relief, with no substantial complications. Apparently, performing the neurectomy also of the AIN does not offer greater advantages compared to the isolated PIN neurectomy.
Keywords: arthritis; hand; pain; upper limb function; wrist.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures


References
-
- Tomaino MM, Miller RJ, Burton RI. Outcome assessment following limited wrist fusion: objective wrist scoring versus patient satisfaction. Contemporary Orthopaedics 199428403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

