Colchicine reduces the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 36917217
- PMCID: PMC10013297
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-023-01718-y
Colchicine reduces the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate whether colchicine treatment was associated with the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in patients with COVID-19.
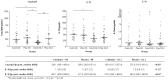
Methods: We present a post hoc analysis from a double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial (RCT) on the effect of colchicine for the treatment of COVID-19. Serum levels of NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome products-active caspase-1 (Casp1p20), IL-1β, and IL-18-were assessed at enrollment and after 48-72 h of treatment in patients receiving standard-of-care (SOC) plus placebo vs. those receiving SOC plus colchicine. The colchicine regimen was 0.5 mg tid for 5 days, followed by 0.5 mg bid for another 5 days.
Results: Thirty-six patients received SOC plus colchicine, and thirty-six received SOC plus placebo. Colchicine reduced the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalization. On Days 2-3, colchicine lowered the serum levels of Casp1p20 and IL-18, but not IL-1β.
Conclusion: Treatment with colchicine inhibited the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, an event triggering the 'cytokine storm' in COVID-19.
Trial registration numbers: RBR-8jyhxh.
Keywords: COVID-19; Colchicine; Cytokines; Inflammasome.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020/05288-6/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2013/08216-2/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2020/04964-8/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2020/04826-4/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 425075/2016-8/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous