Multi-drug resistant ESKAPE pathogens and the uses of plants as their antimicrobial agents
- PMID: 36917278
- PMCID: PMC10013289
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-023-03455-6
Multi-drug resistant ESKAPE pathogens and the uses of plants as their antimicrobial agents
Abstract
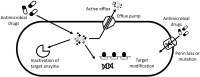
Infections by ESKAPE (Enterococcus sp., Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp.) pathogens cause major concern due to their multi-drug resistance (MDR). The ESKAPE pathogens are frequently linked to greater mortality, diseases, and economic burden in healthcare worldwide. Therefore, the use of plants as a natural source of antimicrobial agents provide a solution as they are easily available and safe to use. These natural drugs can also be enhanced by incorporating silver nanoparticles and combining them with existing antibiotics. By focussing the attention on the ESKAPE organisms, the MDR issue can be addressed much better.
Keywords: Antibiotics; Antimicrobial; ESKAPE; Multi-drug resistance; Pathogen; Plant.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Akter M, Rahman MM, Ullah AKMA, et al. Brassica rapa var. japonica leaf extract mediated green synthesis of crystalline silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their stability, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater. 2018;28:1483–1493. doi: 10.1007/s10904-018-0818-7. - DOI
-
- Baker S, Volova T, Prudnikova SV, et al. Bio-hybridization of nanobactericides with cellulose films for effective treatment against members of ESKAPE multi-drug-resistant pathogens. Appl Nanosci. 2018;8:1101–1110. doi: 10.1007/s13204-018-0717-9. - DOI
-
- Bataineh SMB, Tarazi YH, Ahmad WA. Antibacterial efficacy of some medicinal plants on multidrug resistance bacteria and their toxicity on eukaryotic cells. Appl Sci. 2021;11:8479. doi: 10.3390/app11188479. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous