Outsmarting Pathogens with Antibody Engineering
- PMID: 36917814
- PMCID: PMC10330301
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-101121-084508
Outsmarting Pathogens with Antibody Engineering
Abstract
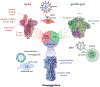
There is growing interest in identifying antibodies that protect against infectious diseases, especially for high-risk individuals and pathogens for which no vaccine is yet available. However, pathogens that manifest as opportunistic or latent infections express complex arrays of virulence-associated proteins and are adept at avoiding immune responses. Some pathogens have developed strategies to selectively destroy antibodies, whereas others create decoy epitopes that trick the host immune system into generating antibodies that are at best nonprotective and at worst enhance pathogenesis. Antibody engineering strategies can thwart these efforts by accessing conserved neutralizing epitopes, generating Fc domains that resist capture or degradation and even accessing pathogens hidden inside cells. Design of pathogen-resistant antibodies can enhance protection and guide development of vaccine immunogens against these complex pathogens. Here, we discuss general strategies for design of antibodies resistant to specific pathogen defense mechanisms.
Keywords: Fc engineering; antibody–drug conjugate; bispecific antibody; immune evasion; passive immunization; vaccines.
Figures
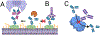
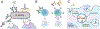
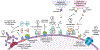
References
-
- Pedrioli A, Oxenius A. 2021. Single B cell technologies for monoclonal antibody discovery. Trends Immunol 42: 1143–58 - PubMed
-
- Zhu Q, McLellan JS, Kallewaard NL, Ulbrandt ND, Palaszynski S, et al. 2017. A highly potent extended half-life antibody as a potential RSV vaccine surrogate for all infants. Sci Transl Med 9: eaaj1928 - PubMed
-
- Bergeron HC, Tripp RA. 2022. Breakthrough therapy designation of nirsevimab for the prevention of lower respiratory tract illness caused by respiratory syncytial virus infections (RSV). Expert Opin Investig Drugs 31: 23–29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

