Wavelet-artificial neural network to predict the acetone sensing by indium oxide/iron oxide nanocomposites
- PMID: 36918606
- PMCID: PMC10015010
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-29898-x
Wavelet-artificial neural network to predict the acetone sensing by indium oxide/iron oxide nanocomposites
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Wavelet-artificial neural network to predict the acetone sensing by indium oxide/iron oxide nanocomposites.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 7;13(1):19271. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46411-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37935799 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
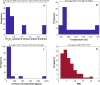
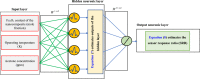
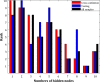
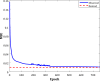
This study applies a hybridized wavelet transform-artificial neural network (WT-ANN) model to simulate the acetone detecting ability of the Indium oxide/Iron oxide (In2O3/Fe2O3) nanocomposite sensors. The WT-ANN has been constructed to extract the sensor resistance ratio (SRR) in the air with respect to the acetone from the nanocomposite chemistry, operating temperature, and acetone concentration. The performed sensitivity analyses demonstrate that a single hidden layer WT-ANN with nine nodes is the highest accurate model for automating the acetone-detecting ability of the In2O3/Fe2O3 sensors. Furthermore, the genetic algorithm has fine-tuned the shape-related parameters of the B-spline wavelet transfer function. This model accurately predicts the SRR of the 119 nanocomposite sensors with a mean absolute error of 0.7, absolute average relative deviation of 10.12%, root mean squared error of 1.14, and correlation coefficient of 0.95813. The In2O3-based nanocomposite with a 15 mol percent of Fe2O3 is the best sensor for detecting acetone at wide temperatures and concentration ranges. This type of reliable estimator is a step toward fully automating the gas-detecting ability of In2O3/Fe2O3 nanocomposite sensors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Liu X, et al. Electrochemical sensor to environmental pollutant of acetone based on Pd-loaded on mesoporous In2O3 architecture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019;290:217–225. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.139. - DOI
-
- Abdi, J., Esmaeili-Faraj, S. H., Mazloom, G. & Pirhoushyaran, T. Metal-organic frameworks for remediation of noxious pollutants. Sustain. Mater. Sens. Remediat. Noxious Pollut. 209–228 (2022).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

