Structure-function relationship and physiological role of apelin and its G protein coupled receptor
- PMID: 36919024
- PMCID: PMC9995629
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-023-01044-x
Structure-function relationship and physiological role of apelin and its G protein coupled receptor
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Structure-function relationship and physiological role of apelin and its G protein coupled receptor.Biophys Rev. 2023 Mar 11;15(2):293-294. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01050-z. eCollection 2023 Apr. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37124918 Free PMC article.
Abstract
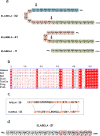
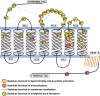
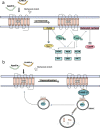
Apelin receptor (APJR) is a class A peptide (apelin) binding G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that plays a significant role in regulating blood pressure, cardiac output, and maintenance of fluid homeostasis. It is activated by a wide range of endogenous peptide isoforms of apelin and elabela. The apelin peptide isoforms contain distinct structural features that aid in ligand recognition and activation of the receptor. Site-directed mutagenesis and structure-based studies have revealed the involvement of extracellular and transmembrane regions of the receptor in binding to the peptide isoforms. The structural features of APJR activation of the receptor as well as mediating G-protein and β-arrestin-mediated signaling are delineated by multiple mutagenesis studies. There is increasing evidence that the structural requirements of APJR to activate G-proteins and β-arrestins are different, leading to biased signaling. APJR also responds to mechanical stimuli in a ligand-independent manner. A multitude of studies has focused on developing both peptide and non-peptide agonists and antagonists specific to APJR. Apelin/elabela-activated APJR orchestrates major signaling pathways such as extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERKs), protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), and p70S. This review focuses on the structural and functional characteristics of apelin, elabela, APJR, and their interactions involved in the binding and activation of the downstream signaling cascade. We also focus on the diverse signaling profile of APJR and its ligands and their involvement in various physiological systems.
Keywords: Apelin receptor; Apelin; Elabela; GPCR; Signaling.
© International Union for Pure and Applied Biophysics (IUPAB) and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023, corrected publication 2023Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

