Abatacept for Delay of Type 1 Diabetes Progression in Stage 1 Relatives at Risk: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 36920087
- PMCID: PMC10154649
- DOI: 10.2337/dc22-2200
Abatacept for Delay of Type 1 Diabetes Progression in Stage 1 Relatives at Risk: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: Previous studies showed that inhibiting lymphocyte costimulation reduces declining β-cell function in individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. We tested whether abatacept would delay or prevent progression of type 1 diabetes from normal glucose tolerance (NGT) to abnormal glucose tolerance (AGT) or to diabetes and the effects of treatment on immune and metabolic responses.
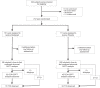
Research design and methods: We conducted a phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-masked trial of abatacept in antibody-positive participants with NGT who received monthly abatacept/placebo infusions for 12 months. The end point was AGT or diabetes, assessed by oral glucose tolerance tests.
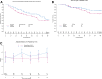
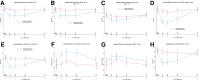
Results: A total of 101 participants received abatacept and 111 placebo. Of these, 81 (35 abatacept and 46 placebo) met the end point of AGT or type 1 diabetes diagnosis (hazard ratio 0.702; 95% CI 0.452, 1.09; P = 0.11) The C-peptide responses to oral glucose tolerance tests were higher in the abatacept arm (P < 0.03). Abatacept reduced the frequency of inducible T-cell costimulatory (ICOS)+ PD1+ T-follicular helper (Tfh) cells during treatment (P < 0.0001), increased naive CD4+ T cells, and also reduced the frequency of CD4+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) from the baseline (P = 0.0067). Twelve months after treatment, the frequency of ICOS+ Tfh, naive CD4+ T cells, and Tregs returned to baseline.
Conclusions: Although abatacept treatment for 1 year did not significantly delay progression to glucose intolerance in at-risk individuals, it impacted immune cell subsets and preserved insulin secretion, suggesting that costimulation blockade may modify progression of type 1 diabetes.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Response to Comment on Russell et al. Abatacept for Delay of Type 1 Diabetes Progression in Stage 1 Relatives at Risk: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2023;46:1005-1013.Diabetes Care. 2023 Nov 1;46(11):e210-e211. doi: 10.2337/dci23-0050. Diabetes Care. 2023. PMID: 37890101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on Russell et al. Abatacept for Delay of Type 1 Diabetes Progression in Stage 1 Relatives at Risk: A Randomized, Double-Masked, Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2023;46:1005-1013.Diabetes Care. 2023 Nov 1;46(11):e209. doi: 10.2337/dc23-1115. Diabetes Care. 2023. PMID: 37890102 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bluestone JA, Buckner JH, Herold KC. Immunotherapy: building a bridge to a cure for type 1 diabetes. Science 2021;373:510–516 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK097835/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061037/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060916/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060782/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI109565/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061030/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001872/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001855/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061029/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061035/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

