Novel Once-Weekly Basal Insulin Fc Achieved Similar Glycemic Control With a Safety Profile Comparable to Insulin Degludec in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 36920867
- PMCID: PMC10154655
- DOI: 10.2337/dc22-2395
Novel Once-Weekly Basal Insulin Fc Achieved Similar Glycemic Control With a Safety Profile Comparable to Insulin Degludec in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Basal Insulin Fc (BIF; insulin efsitora alfa; LY3209590), a fusion protein combining a novel single-chain insulin variant with a human IgG Fc domain, is designed for once-weekly basal insulin administration. This phase 2 study assessed safety and efficacy of BIF versus degludec in 265 patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) using multiple daily injections.
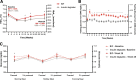
Research design and methods: During this randomized, parallel, open-label study, patients with T1D were randomized (1:1) to receive BIF once weekly or degludec once daily over the 26-week treatment period. Both groups were titrated to a fasting glucose level of 80-100 mg/dL. The primary end point was HbA1c change from baseline to week 26 (noninferiority margin, 0.4%). Secondary end points included percent time in range (TIR) (70-180 mg/dL), continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) fasting glucose (FG) level, and rate of hypoglycemia.
Results: After 26 weeks, patients receiving BIF had noninferior HbA1c change from baseline versus those receiving degludec, with a statistically significant treatment difference of 0.17% (90% CI 0.01, 0.32; P = 0.07) favoring the comparator. Percent TIR was similar for patients in the BIF (56.1%) and degludec (58.9%; P = 0.112) groups at week 26. FG values were significantly higher for patients receiving BIF (158.8 mg/dL) versus degludec (143.2 mg/dL; P = 0.003). Rates of CGM-derived hypoglycemia were not statistically significantly different for BIF and degludec over 24 h for level 1 (P = 0.960) or level 2 (P = 0.517) hypoglycemia during the treatment period. Occurrence of serious adverse events was similar between the BIF and degludec groups.
Conclusions: Once-weekly BIF demonstrated noninferior glycemic control to once-daily degludec (treatment difference: 0.17% favoring degludec) and no difference in hypoglycemia or other safety findings in patients with T1D.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
In type 1 diabetes, weekly basal insulin Fc was noninferior to daily insulin degludec for HbA1c at 26 wk.Ann Intern Med. 2023 Jul;176(7):JC80. doi: 10.7326/J23-0045. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Ann Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37399552
References
-
- American Diabetes Association . 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl. 1):S111–S124 - PubMed
-
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group . Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in a clinical care environment: evidence from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring (JDRF-CGM) trial. Diabetes Care 2010;33:17–22 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oldham V, Mumford B, Lee D, Jones J, Das G. Impact of insulin pump therapy on key parameters of diabetes management and diabetes related emotional distress in the first 12 months. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020;166:108281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

