Interpreting Image-based Profiles using Similarity Clustering and Single-Cell Visualization
- PMID: 36921124
- PMCID: PMC10027367
- DOI: 10.1002/cpz1.713
Interpreting Image-based Profiles using Similarity Clustering and Single-Cell Visualization
Abstract
Image-based profiling quantitatively assesses the effects of perturbations on cells by capturing a breadth of changes via microscopy. Here, we provide two complementary protocols to help explore and interpret data from image-based profiling experiments. In the first protocol, we examine the similarity among perturbed cell samples using data from compounds that cluster by their mechanisms of action. The protocol includes steps to examine feature-driving differences between samples and to visualize correlations between features and treatments to create interpretable heatmaps using the open-source web tool Morpheus. In the second protocol, we show how to interactively explore images together with the numerical data, and we provide scripts to create visualizations of representative single cells and image sites to understand how changes in features are reflected in the images. Together, these two tutorials help researchers interpret image-based data to speed up research. © 2023 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC. Basic Protocol 1: Exploratory analysis of profile similarities and driving features Basic Protocol 2: Image and single-cell visualization following profile interpretation.
Keywords: Morpheus; high-dimensional data; image-based profiling; morphological analysis; profiling; single-cell visualization.
© 2023 The Authors. Current Protocols published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT:
SS and AEC serve as scientific advisors for companies that use image-based profiling and Cell Painting (AEC: Recursion, SS: Waypoint Bio, Dewpoint Therapeutics) and receive honoraria for occasional talks at pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies.
Figures
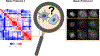



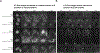

References
-
- Azarenko O, Smiyun G, Mah J, Wilson L, and Jordan MA 2014. Antiproliferative mechanism of action of the novel taxane cabazitaxel as compared with the parent compound docetaxel in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Molecular cancer therapeutics 13:2092–2103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

