3Cpro of FMDV inhibits type II interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling pathway by blocking STAT1 nuclear translocation
- PMID: 36921803
- PMCID: PMC10311264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.03.003
3Cpro of FMDV inhibits type II interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling pathway by blocking STAT1 nuclear translocation
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "3Cpro of FMDV inhibits type II interferon-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling pathway by blocking STAT1 nuclear translocation" [Virol Sin 38 (2023) 387-397].Virol Sin. 2024 Apr;39(2):351-354. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.12.007. Epub 2024 Jan 27. Virol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38281821 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
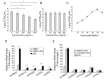
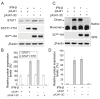
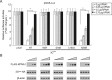
Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) has developed various strategies to antagonize the host innate immunity. FMDV Lpro and 3Cpro interfere with type I IFNs through different mechanisms. The structural protein VP3 of FMDV degrades Janus kinase 1 to suppress IFN-γ signaling transduction. Whether non-structural proteins of FMDV are involved in restraining type II IFN signaling pathways is unknown. In this study, it was shown that FMDV replication was resistant to IFN-γ treatment after the infection was established and FMDV inhibited type II IFN induced expression of IFN-γ-stimulated genes (ISGs). We also showed for the first time that FMDV non-structural protein 3C antagonized IFN-γ-stimulated JAK-STAT signaling pathway by blocking STAT1 nuclear translocation. 3Cpro expression significantly reduced the ISGs transcript levels and palindromic gamma-activated sequences (GAS) promoter activity, without affecting the protein level, tyrosine phosphorylation, and homodimerization of STAT1. Finally, we provided evidence that 3C protease activity played an essential role in degrading KPNA1 and thus inhibited ISGs mRNA and GAS promoter activities. Our results reveal a novel mechanism by which an FMDV non-structural protein antagonizes host type II IFN signaling.
Keywords: 3C; Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV); IFN-γ; JAK-STAT signaling pathway; KPNA1; STAT1.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Aaronson D.S., Horvath C.M. A road map for those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 2002;296:1653–1655. - PubMed
-
- Begitt A., Droescher M., Meyer T., Schmid C.D., Baker M., Antunes F., Knobeloch K.P., Owen M.R., Naumann R., Decker T., Vinkemeier U. STAT1-cooperative DNA binding distinguishes type 1 from type 2 interferon signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2014;15:168–176. - PubMed
-
- Belsham G.J. Translation and replication of FMDV RNA. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005;288:43–70. - PubMed
-
- Birtley J.R., Knox S.R., Jaulent A.M., Brick P., Leatherbarrow R.J., Curry S. Crystal structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus 3C protease. New insights into catalytic mechanism and cleavage specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:11520–11527. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

