Oxygen Therapy in Pulmonary Vascular Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Comment
- PMID: 36922056
- PMCID: PMC9988711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hfc.2022.11.001
Oxygen Therapy in Pulmonary Vascular Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Comment
Abstract
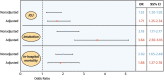
Main pulmonary vascular diseases (PVD) with precapillary pulmonary hypertension (PH) are pulmonary arterial and chronic thromboembolic PH. Guidelines recommend supplemental oxygen therapy (SOT) for severely hypoxemic patients with PH, but evidence is scarce. The authors performed a systematic review and where possible meta-analyses on the effects of SOT on hemodynamics and exercise performance in patients with PVD. In PVD, short-term SOT significantly improved mean pulmonary artery pressure and exercise performance. There is growing evidence on the benefit of long-term SOT for selected patients with PVD regarding exercise capacity and maybe even survival.
Keywords: Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; Hyperoxia; Long-term oxygen therapy; Oxygen; Oxygen therapy; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Pulmonary hypertension; Pulmonary vascular disease.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- CDC COVID Data Tracker: Home. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home. Accessed December 25, 2022.
-
- Clerkin K.J., Fried J.A., Raikhelkar J., et al. COVID-19 and Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 2020;141(20):1648–1655. - PubMed
-
- Madjid M., Safavi-Naeini P., Solomon S.D., et al. Potential Effects of Coronaviruses on the Cardiovascular System. JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(7):831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical