Bone collagen quality in lumbar fusion patients: the association between volumetric bone mineral density and advanced glycation endproducts
- PMID: 36922425
- PMCID: PMC10623215
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-023-07589-5
Bone collagen quality in lumbar fusion patients: the association between volumetric bone mineral density and advanced glycation endproducts
Abstract
Purpose: The sole determination of volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) is insufficient to evaluate overall bone integrity. The accumulation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs) stiffens and embrittles collagen fibers. Despite the important role of AGEs in bone aging, the relationship between AGEs and vBMD is poorly understood. We hypothesized that an accumulation of AGEs, a marker of impaired bone quality, is related to decreased vBMD.
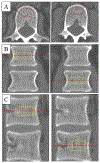
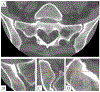
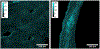
Methods: Prospectively collected data of 127 patients undergoing lumbar fusion were analyzed. Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) measurements were performed at the lumbar spine. Intraoperative bone biopsies were obtained and analyzed with confocal fluorescence microscopy for fluorescent AGEs, both trabecular and cortical. Spearman's correlation coefficients were calculated to examine relationships between vBMD and fAGEs, stratified by sex. Multivariable linear regression analysis with adjustments for age, sex, body mass index (BMI), race, diabetes mellitus and HbA1c was used to investigate associations between vBMD and fAGEs.
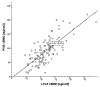
Results: One-hundred and twenty-seven patients (51.2% female, 61.2 years, BMI of 28.7 kg/m2) with 107 bone biopsies were included in the final analysis, excluding patients on anti-osteoporotic drug therapy. In the univariate analysis, cortical fAGEs increased with decreasing vBMD at (r = -0.301; p = 0.030), but only in men. In the multivariable analysis, trabecular fAGEs increased with decreasing vBMD after adjusting for age, sex, BMI, race, diabetes mellitus and HbA1c (β = 0.99;95%CI=(0.994,1.000); p = 0.04).
Conclusion: QCT-derived vBMD measurements were found to be inversely associated with trabecular fAGEs. Our results enhance the understanding of bone integrity by suggesting that spine surgery patients with decreased bone quantity may also have poorer bone quality.
Keywords: Bone quality; Confocal fluorescence microscopy; Confocal mapping; Non-enzymatic collagen cross-linking; QCT; Quantitative computed tomography.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest concerning materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper. Dr. Sama reports royalties from Ortho Development, Corp.; private investments for Vestia Ventures MiRUS Investment, LLC, ISPH II, LLC, ISPH 3, LLC and VBros Venture Partners X Centinel Spine; consulting fee from Clariance, Inc., Kuros Biosciences AG and Medical Device Business Service, Inc.; speaking and teaching arrangements of DePuy Synthes Products, Inc.; membership of scientific advisory board of Clariance, Inc., and Kuros Biosciences AG; and trips/travel of Medical Device Business research support from Spinal Kinetics, Inc., outside the submitted work. Dr. Cammisa reports royalties from NuVasive, Inc.; private investments for 4WEB Medical/4WEB, Inc., Bonovo Orthopedics, Inc., Healthpoint Capital Partners, LP, ISPH II, LLC, ISPH 3 Holdings, LLC, Ivy Healthcare Capital Partners, LLC, Medical Device Partners II, LLC, Medical Device Partners III, LLC, Orthobond Corporation, Spine Biopharma, LLC, Synexis, LLC, Tissue Differentiation Intelligence, LLC, VBVP VI, LLC, VBVP X, LLC (Centinel) and Woven Orthopedics Technologies; consulting fees from 4WEB Medical/4WEB, Inc., DePuy Synthes Spine, NuVasive, Inc., Spine Biopharma, LLC and Synexis, LLC; membership of scientific advisory board/other office of Healthpoint Capital Partners, LP, Medical Device Partners III, LLC, Orthobond Corporation, Spine Biopharma, LLC, Synexis, LLC and Woven Orthopedic Technologies; and research support from 4WEB Medical/4WEB, Inc., Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Camber Spine and Centinel Spine, outside the submitted work. Dr. Girardi reports royalties from Lanx, Inc., and Ortho Development Corp.; private investments for Centinel Spine and BCMID; stock ownership of Healthpoint Capital Partners, LP; and consulting fees from NuVasive, Inc., and DePuy Synthes Spine, outside the submitted work. Dr. Hughes reports research support from NuVasive, Inc., and Kuros Biosciences AG and fellowship support from NuVasive, Inc., and Kuros Biosciences AG, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Liu J et al. (2022) Heavy clinical and economic burden of osteoporotic fracture among elderly female Medicare beneficiaries. Osteoporos Int 33(2):413–423 - PubMed
-
- Johnell O, Kanis JA (2006) An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int 17(12):1726–1733 - PubMed
-
- Burge R et al. (2007) Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005–2025. J Bone Miner Res 22(3):465–175 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

