MALT1-dependent cleavage of CYLD promotes NF-κB signaling and growth of aggressive B-cell receptor-dependent lymphomas
- PMID: 36922488
- PMCID: PMC10017792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-023-00809-7
MALT1-dependent cleavage of CYLD promotes NF-κB signaling and growth of aggressive B-cell receptor-dependent lymphomas
Abstract
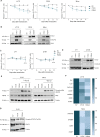
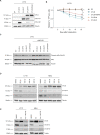
The paracaspase mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 1 (MALT1) is a protease and scaffold protein essential in propagating B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling to NF-κB. The deubiquitinating enzyme cylindromatosis (CYLD) is a recently discovered MALT1 target that can negatively regulate NF-κB activation. Here, we show that low expression of CYLD is associated with inferior prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients, and that chronic BCR signaling propagates MALT1-mediated cleavage and, consequently, inactivation and rapid proteasomal degradation of CYLD. Ectopic overexpression of WT CYLD or a MALT1-cleavage resistant mutant of CYLD reduced phosphorylation of IκBα, repressed transcription of canonical NF-κB target genes and impaired growth of BCR-dependent lymphoma cell lines. Furthermore, silencing of CYLD expression rendered BCR-dependent lymphoma cell lines less sensitive to inhibition of NF-κΒ signaling and cell proliferation by BCR pathway inhibitors, e.g., the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib, indicating that these effects are partially mediated by CYLD. Taken together, our findings identify an important role for MALT1-mediated CYLD cleavage in BCR signaling, NF-κB activation and cell proliferation, which provides novel insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms and clinical potential of inhibitors of MALT1 and ubiquitination enzymes as promising therapeutics for DLBCL, MCL and potentially other B-cell malignancies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

