Novel hybrid evolutionary algorithm for bi-objective optimization problems
- PMID: 36922545
- PMCID: PMC10017715
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-31123-8
Novel hybrid evolutionary algorithm for bi-objective optimization problems
Abstract
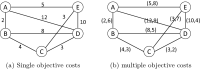
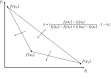
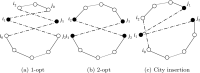
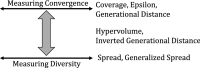
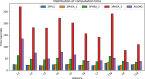
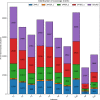
This work considers the Bi-objective Traveling Salesman Problem (BTSP), where two conflicting objectives, the travel time and monetary cost between cities, are minimized. Our purpose is to compute the trade-off solutions that fulfill the problem requirements. We introduce a novel three-Phase Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithm (3PHEA) based on the Lin-Kernighan Heuristic, an improved version of the Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm, and Pareto Variable Neighborhood Search, a multi-objective version of VNS. We conduct a comparative study with three existing approaches dedicated to solving BTSP. To assess the performance of algorithms, we consider 20 BTSP instances from the literature of varying degrees of difficulty (e.g., euclidean, random, mixed, etc.) and different sizes ranging from 100 to 1000 cities. We also compute several multi-objective performance indicators, including running time, coverage, hypervolume, epsilon, generational distance, inverted generational distance, spread, and generalized spread. Experimental results and comparative analysis indicate that the proposed three-phase method 3PHEA is significantly superior to existing approaches covering up to 80% of the true Pareto fronts.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Matai R, Singh SP, Mittal ML. Traveling salesman problem: An overview of applications, formulations, and solution approaches. Travel. Salesman Probl. Theory Appl. 2010 doi: 10.5772/12909. - DOI
-
- Alexandridis A, Paizis E, Chondrodima E, Stogiannos M. A particle swarm optimization approach in printed circuit board thermal design. Integrat. Comput. Aided Eng. 2017;24(2):143–155. doi: 10.3233/ICA-160536. - DOI
-
- Carpio, R. F., Maiolini, J., Potena, C., Garone, E., Ulivi, G., Gasparn, A. Mp-stsp: A multi-platform steiner traveling salesman problem formulation for precision agriculture in orchards. In 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp 2345–2351 (2021). 10.1109/ICRA48506.2021.9561023.
-
- Mosayebi M, Sodhi M, Wettergren TA. The traveling salesman problem with job-times (tspj) Comput. Oper. Res. 2021;129:105226. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2021.105226. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

