Symbiotic electroneural and musculoskeletal framework to encode proprioception via neurostimulation: ProprioStim
- PMID: 36923003
- PMCID: PMC10009292
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106248
Symbiotic electroneural and musculoskeletal framework to encode proprioception via neurostimulation: ProprioStim
Abstract
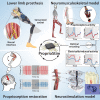
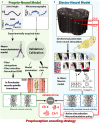
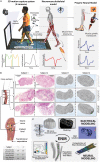
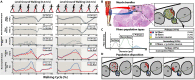
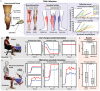
Peripheral nerve stimulation in amputees achieved the restoration of touch, but not proprioception, which is critical in locomotion. A plausible reason is the lack of means to artificially replicate the complex activity of proprioceptors. To uncover this, we coupled neuromuscular models from ten subjects and nerve histologies from two implanted amputees to develop ProprioStim: a framework to encode proprioception by electrical evoking neural activity in close agreement with natural proprioceptive activity. We demonstrated its feasibility through non-invasive stimulation on seven healthy subjects comparing it with standard linear charge encoding. Results showed that ProprioStim multichannel stimulation was felt more natural, and hold promises for increasing accuracy in knee angle tracking, especially in future implantable solutions. Additionally, we quantified the importance of realistic 3D-nerve models against extruded models previously adopted for further design and validation of novel neurostimulation encoding strategies. ProprioStim provides clear guidelines for the development of neurostimulation policies restoring natural proprioception.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Bioelectronics; Clinical neuroscience.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.R. holds shares of “Sensars Neuroprosthetics,” a start-up company dealing with potential commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs. The other authors do not have anything to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Farina D., Vujaklija I., Sartori M., Kapelner T., Negro F., Jiang N., Bergmeister K., Andalib A., Principe J., Aszmann O.C. Man/machine interface based on the discharge timings of spinal motor neurons after targeted muscle reinnervation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017;1 doi: 10.1038/s41551-016-0025. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

