FGF19-mediated ELF4 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through transactivating FGFR4 and SRC
- PMID: 36923538
- PMCID: PMC10008733
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.82269
FGF19-mediated ELF4 overexpression promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through transactivating FGFR4 and SRC
Abstract
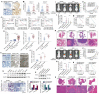
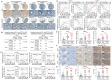
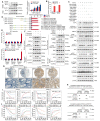
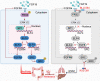
Background: Metastasis accounts for the high lethality of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. Unfortunately, the molecular mechanism manipulating metastasis in CRC is still elusive. Here, we investigated the function of E74-like factor 4 (ELF4), an ETS family member, in facilitating CRC progression. Methods: The expression of ELF4 in human CRC samples and CRC cell lines was determined by quantitative real-time PCR, immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting. The migratory and invasive phenotypes of CRC cells were evaluated by in vitro transwell assays and in vivo metastatic models. The RNA sequencing was used to explore the downstream targets of ELF4. The luciferase reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were used to ascertain the transcriptional regulation related to ELF4. Results: We found elevated ELF4 was positively correlated with distant metastasis, advanced AJCC stages, and dismal outcomes in CRC patients. ELF4 expression was also an independent predictor of poor prognosis. Overexpression of ELF4 boosted CRC metastasis via transactivating its downstream target genes, fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 (FGFR4) and SRC proto-oncogene, non-receptor tyrosine kinase, SRC. Fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) upregulated ELF4 expression through the ERK1/2/SP1 axis. Clinically, ELF4 expression had a positive correlation with FGF19, FGFR4 and SRC, and CRC patients who positively coexpressed FGF19/ELF4, ELF4/FGFR4, or ELF4/SRC exhibited the worst clinical outcomes. Furthermore, the combination of the FGFR4 inhibitor BLU-554 and the SRC inhibitor KX2-391 dramatically suppressed ELF4-mediated CRC metastasis. Conclusions: We demonstrated the essentiality of ELF4 in the metastatic process of CRC, and targeting the ELF4-relevant positive feedback circuit might represent a novel therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: BLU-554; Colorectal cancer; E74-like factor 4; Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4; Metastasis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Biller LH, Schrag D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325:669–85. - PubMed
-
- Ferrarotto R, Pathak P, Maru D, Agarwal A, Overman M, Hoff PM. et al. Durable complete responses in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with chemotherapy alone. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011;10:178–82. - PubMed
-
- Propper DJ, Gao F, Saunders MP, Sarker D, Hartley JA, Spanswick VJ. et al. PANTHER: AZD8931, inhibitor of EGFR, ERBB2 and ERBB3 signalling, combined with FOLFIRI: a Phase I/II study to determine the importance of schedule and activity in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2022 [Epub ahead of print] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oikawa T, Yamada T. Molecular biology of the Ets family of transcription factors. Gene. 2003;303:11–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

