Exploring the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of action of sinomenium acutum in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on systems biology and network pharmacology
- PMID: 36923645
- PMCID: PMC10009275
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1065171
Exploring the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of action of sinomenium acutum in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on systems biology and network pharmacology
Abstract
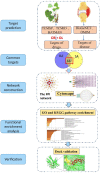
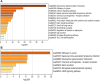
Objective: To investigate and predict the targets and signaling pathways of sinomenium acutum (SA) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) through systems biology and network pharmacology, and to elucidate its possible mechanisms of action. Methods: We screened the active ingredients and corresponding target proteins of SA in Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP), Traditional Chinese Medicines Integrated Database (TCMID) and Bioinformatics Analysis Tool for Molecular mechANism of Traditional Chinese Medicine (BATMAN); and obtained the targets of rheumatoid arthritis diseases in a database of gene-disease associations (DisGeNET), Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database. The two targets were mapped by Venn diagram and the intersection was taken. The intersecting targets were used to construct protein-protein interaction (PPI) network maps in the String database, and Metascape was used for Gene Ontology (GO) functional annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment. Finally, the molecular docking technique was applied to validate and further clarify the core target of SA for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Results: A total of six active ingredients and 217 potential targets were obtained after screening; 2,752 rheumatoid arthritis-related targets and 66 targets common to RA and SA. GO function and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis yielded 751 GO function entries (652 GO biological processes, 59 GO molecular functions and 40 GO cellular components) and 77 KEGG signaling pathways. It mainly involves pathways related to neural activity ligand-receptor interaction pathways, cancer pathways, calcium signaling channels, Th17 cell differentiation and others, which are mainly classified into four categories, including regulation of immunity, anti-inflammation, regulation of cell growth and apoptosis, and signaling. The molecular docking results showed that the binding energy of PTGS2, CASP3, JUN and PPARG to the key components beta-sitosterol, 16-epi-Isositsirikine, Sinomenine and Stepholidine were ≤ -6.5 kcal/mol, suggesting the existence of molecular binding sites. Conclusion: SA acts on key targets such as PTGS2, CASP3, JUN, and PPARG to modulate signaling pathways such as neural activity ligand-receptor interaction, cancer, calcium ion, NF-κB, and Th17 cell differentiation to regulate immunity, anti-inflammation, modulation of cell cycle, bone metabolism, and signaling for the treatment of RA. It was also confirmed that the treatment of RA with SA has multi-component, multi-target, multi-pathway and multi-mechanism characteristics.
Keywords: molecular docking; network pharmacology; rheumatoid arthritis; sinomenium acutum; target.
Copyright © 2023 Gong, Wang, An and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Chen X. M., Huang R. Y., Huang Q. C., Chu Y. L., Yan J. Y. (2015). Systemic review and meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and adverse effects of zhengqing fengtongning combined with methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 910376. [Journal Article; Review]. 10.1155/2015/910376 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chunwei W., Li L., Shengwang L., Chao C., Shumei W. (2016). Application of drug target prediction technology in the network pharmacology of Chinese medicine. China J. Chin. Materia Medica 41 (03), 377–382. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

