Care Bundle to Improve Oxygen Maintenance and Events
- PMID: 36926217
- PMCID: PMC10013622
- DOI: 10.1097/pq9.0000000000000639
Care Bundle to Improve Oxygen Maintenance and Events
Abstract
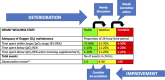
Prolonged periods spent outside the target range of oxygen saturation (SpO2) in preterm infants, along with frequent desaturation events, predispose them to retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) and long-term neurodevelopmental impairment. The primary aim of this study was to increase the mean time spent within the target SpO2 range (WTR) by 10% and to reduce the frequency of desaturation events by 5 events per patient day, respectively, within 18 months of implementing a care bundle.
Methods: This study was completed in a 46-bed neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), involving 246 staff members and led by a quality improvement team. The change interventions included implementing new practice guidelines, reviewing daily summaries of SpO2 maintenance, daily infant wellness assessment, standardizing workflow, and responding to SpO2 alarms. In addition, we collected staff satisfaction and compliance with change interventions, resource use, and morbidity and mortality data at discharge.
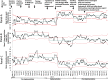
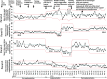
Results: The mean time spent WTR increased from 65.3% to 75.3%, and the frequency of desaturation events decreased from 25.1 to 16.5 events per patient day, respectively, with a higher magnitude of benefit in infants on days with supplemental oxygen. Postimplementation, the duration of high-frequency ventilation and supplemental oxygen were lower, but morbidity and mortality rates were similar. Staff satisfaction with training workshops, coaching, use of the infant wellness assessment tool, and SpO2 alarm management algorithms were 74%, 82%, 80%, and 74%, respectively.
Conclusion: Implementing a care bundle to improve oxygen maintenance and reduce desaturation events increased the time spent WTR and reduced the frequency of desaturation events.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Askie LM, Darlow BA, Finer N, et al. ; Neonatal Oxygenation Prospective Meta-analysis (NeOProM) Collaboration. Association between oxygen saturation targeting and death or disability in extremely preterm infants in the neonatal oxygenation prospective meta-analysis collaboration. JAMA. 2018;319:2190–2201. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Flynn JT, Bancalari E, Snyder ES, et al. . A cohort study of transcutaneous oxygen tension and the incidence and severity of retinopathy of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:1050–1054. - PubMed
-
- Saugstad OD. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia-oxidative stress and antioxidants. Semin Neonatol. 2003;8:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Mccolm JR, Fleck BW. Retinopathy of prematurity: causation. Semin Neonatol. 2001;6:453–460. - PubMed
-
- McColm JR, Cunningham S, Wade J, et al. . Hypoxic oxygen fluctuations produce less severe retinopathy than hyperoxic fluctuations in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity. Pediatr Res. 2004;55:107–113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
