Long-term adaptive response in COVID-19 vaccine recipients and the effect of a booster dose
- PMID: 36926327
- PMCID: PMC10011096
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1123158
Long-term adaptive response in COVID-19 vaccine recipients and the effect of a booster dose
Abstract
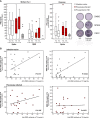
We examined the immune response in subjects previously infected with SARS-CoV2 and infection-naïve 9 months after primary 2-dose COVID-19 mRNA vaccination and 3 months after the booster dose in a longitudinal cohort of healthcare workers. Nine months after primary vaccination, previously infected subjects exhibited higher residual antibody levels, with significant neutralizing activity against distinct variants compared to infection-naïve subjects. The higher humoral response was associated with higher levels of receptor binding domain (RBD)-specific IgG+ and IgA+ memory B cells. The booster dose increased neither neutralizing activity, nor the B and T cell frequencies. Conversely, infection-naïve subjects needed the booster to achieve comparable levels of neutralizing antibodies as those found in previously infected subjects after primary vaccination. The neutralizing titer correlated with anti-RBD IFNγ producing T cells, in the face of sustained B cell response. Notably, pre-pandemic samples showed high Omicron cross-reactivity. These data show the importance of the booster dose in reinforcing immunological memory and increasing circulating antibodies in infection-naïve subjects.
Keywords: COVID-19; Delta; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; T and B cells; mRNA vaccine; neutralizing antibodies.
Copyright © 2023 Perico, Todeschini, Casiraghi, Mister, Pezzotta, Peracchi, Tomasoni, Trionfini, Benigni and Remuzzi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- COVID-19 map. Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

