Efficacy of azithromycin in treating Ureaplasma urealyticum: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36927441
- PMCID: PMC10021952
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08102-5
Efficacy of azithromycin in treating Ureaplasma urealyticum: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Ureaplasma urealyticum is the most prevalent genital mycoplasma isolated from the urogenital tract of females, but there is no unified treatment plan. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of azithromycin in treating Ureaplasma urealyticum.
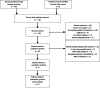
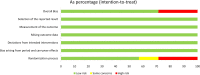
Methods: From the earliest to June 2022, published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on azithromycin treatment of Ureaplasma urealyticum were retrieved by searching PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. Two reviewers independently extracted the data. We utilized the Cochrane risk-of-bias assessment technique to assess the quality of included RCTs. The data were analyzed using the R language (version 4.0.4) software.
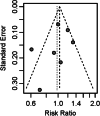
Results: Seven RCTs were finally included, involving 512 participants (240 in the experimental group, 272 in the control group). The experimental group was treated with azithromycin monotherapy, while the control group was treated with doxycycline or a placebo. Meta-analysis results suggested that azithromycin has a comparable therapeutic effect on Ureaplasma urealyticum in comparison to that of controls (risk ratio [RR] = 1.03, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.94-1.12). Subgroup analysis showed that the dose and duration of azithromycin may don't affect its efficacy.
Conclusion: Regarding the meta-analysis that we performed based on existing clinical studies, azithromycin is quite effective in treating Ureaplasma urealyticum.
Keywords: Azithromycin; Efficacy; Female; Meta-analysis; Ureaplasma urealyticum.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of azithromycin in reducing lower genital Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization in women at risk for preterm delivery.J Matern Fetal Med. 1999 Jan-Feb;8(1):12-6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199901/02)8:1<12::AID-MFM3>3.0.CO;2-8. J Matern Fetal Med. 1999. PMID: 10052839 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative randomized pilot study of azithromycin and doxycycline efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of prostate infection caused by Ureaplasma urealyticum.Chemotherapy. 2006;52(1):9-11. doi: 10.1159/000090234. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Chemotherapy. 2006. PMID: 16340190 Clinical Trial.
-
Azithromycin for empirical treatment of the nongonococcal urethritis syndrome in men. A randomized double-blind study.JAMA. 1995 Aug 16;274(7):545-9. JAMA. 1995. PMID: 7629982 Clinical Trial.
-
Resistance to tetracyclines among clinical isolates of Mycoplasma hominis and Ureaplasma species: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Mar 12;76(4):865-875. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa538. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33367765
-
Association of Ureaplasma urealyticum colonization with development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systemic review and meta-analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014 Apr;34(2):265-269. doi: 10.1007/s11596-014-1269-1. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24710943
Cited by
-
[Clinical characteristics of Ureaplasma urealyticum infection and colonization in extremely preterm infants].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 15;26(8):811-816. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2403002. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39148384 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Strauss M, Colodner R, Sagas D, Adawi A, Edelstein H, Chazan B. Detection of Ureaplasma Species by a semi-quantitative PCR test in urine samples: can it predict clinical significance? Isr Med Assoc J IMAJ. 2018;20(1):9–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

