Evolution and functional diversification of yeast sugar transporters
- PMID: 36928992
- PMCID: PMC10500205
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20220233
Evolution and functional diversification of yeast sugar transporters
Abstract
While simple sugars such as monosaccharides and disaccharide are the typical carbon source for most yeasts, whether a species can grow on a particular sugar is generally a consequence of presence or absence of a suitable transporter to enable its uptake. The most common transporters that mediate sugar import in yeasts belong to the major facilitator superfamily (MFS). Some of these, for example the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hxt proteins have been extensively studied, but detailed information on many others is sparce. In part, this is because there are many lineages of MFS transporters that are either absent from, or poorly represented in, the model S. cerevisiae, which actually has quite a restricted substrate range. It is important to address this knowledge gap to gain better understanding of the evolution of yeasts and to take advantage of sugar transporters to exploit or engineer yeasts for biotechnological applications. This article examines the full repertoire of MFS proteins in representative budding yeasts (Saccharomycotina). A comprehensive analysis of 139 putative sugar transporters retrieved from 10 complete genomes sheds new light on the diversity and evolution of this family. Using the phylogenetic lens, it is apparent that proteins have often been misassigned putative functions and this can now be corrected. It is also often seen that patterns of expansion of particular genes reflects the differential importance of transport of specific sugars (and related molecules) in different yeasts, and this knowledge also provides an improved resource for the selection or design of tailored transporters.
Keywords: Major Facilitator Superfamily; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; biotechnology; glucose transport; transport.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
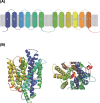

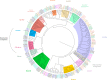

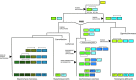



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

