Scleral Proteome in Noninfectious Scleritis Unravels Upregulation of Filaggrin-2 and Signs of Neovascularization
- PMID: 36930145
- PMCID: PMC10036950
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.3.27
Scleral Proteome in Noninfectious Scleritis Unravels Upregulation of Filaggrin-2 and Signs of Neovascularization
Abstract
Purpose: Scleritis is a severe inflammatory ocular disorder with unknown pathogenesis. We investigated healthy sclera as well as sclera affected by noninfectious scleritis for differentially expressed proteins using a mass spectrometry approach.
Methods: We collected scleral samples of enucleated eyes due to severe noninfectious scleritis (n = 3), and control scleral tissues (n = 5), all exenterated eyes for eyelid carcinomas (n = 4), or choroidal melanoma (n = 1) without scleral invasion. Samples were prepared for the nano liquid-chromatography mass spectrometer (LC-MS), data were analyzed using proteomics software (Scaffold), and is available via ProteomeXchange (identifier PXD038727). Samples were also stained for immuno-histopathological evaluation.
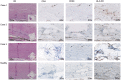
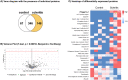
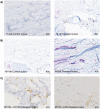
Results: Mass spectrometry identified 629 proteins within the healthy and diseased scleral tissues, whereof collagen type XII, VI, and I were the most abundantly expressed protein. Collagen type II-XII was also present. Filaggrin-2, a protein that plays a crucial role in epidermal barrier function, was found upregulated in all scleritis cases. In addition, other epithelial associated proteins were upregulated (such as keratin 33b, 34, and 85, epiplakin, transglutaminase-3, galectin 7, and caspase-14) in scleritis. Further, upregulated proteins involved in regulation of the cytoskeleton (vinculin and myosin 9), and housekeeping proteins were found (elongation factor-2 and cytoplasmic dynein 1) in our study. Upregulation of filaggrin-2 and myosin-9 was confirmed with immunohistochemistry, the latter protein showing co-localization with the endothelial cell marker ETC-related gene (ERG), indicating neovascularization in scleral tissue affected by scleritis.
Conclusions: We found upregulation of filaggrin-2 and signs of neovascularization in scleral tissue of patients with noninfectious scleritis. Further research, ideally including more scleritis cases, is needed to validate our findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures

References
-
- Wakefield D, Di Girolamo N, Thurau S, Wildner G, McCluskey P.. Scleritis: Immunopathogenesis and molecular basis for therapy. Prog Retinal Eye Res. 2013; 35: 44–62. - PubMed
-
- Hankins M, Margo CE.. Histopathological evaluation of scleritis review. J Clin Pathol. 2019; 72: 386–390. - PubMed
-
- Rao NA, Marak GE, Hidayat AA.. Necrotizing scleritis. A clinico-pathologic study of 41 cases. Ophthalmology. 1985; 92: 1542–1549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

