Digital spatial profiling of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Toward a molecular framework for risk stratification
- PMID: 36930707
- PMCID: PMC10022906
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade4582
Digital spatial profiling of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Toward a molecular framework for risk stratification
Abstract
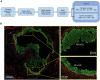
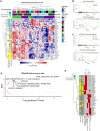
The histopathologic heterogeneity of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) complicates the prediction of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) risk. Intratumoral regions of pancreaticobiliary (PB), intestinal (INT), and gastric foveolar (GF) epithelium may occur with either low-grade dysplasia (LGD) or high-grade dysplasia (HGD). We used digital spatial RNA profiling of dysplastic epithelium (83 regions) from surgically resected IPMN tissues (12 patients) to differentiate subtypes and predict genes associated with malignancy. The expression patterns of PB and GF lesions diverged from INT, suggesting that PB and GF arise from a common lineage. Transcriptional dysregulation within PB lesions mirrored that of PDAC, whereas INT and GF foci did not. Tumor necrosis factor/nuclear factor κB (TNF-NFκB) and cell cycle (cycling S and cycling G2-M) programs occurred with relative prominence in PB and INT subtypes, respectively. Together, this study delineates markers of high-risk IPMN and insights into malignant progression.
Figures




References
-
- R. L. Siegel, K. D. Miller, H. E. Fuchs, A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72, 7–33 (2022). - PubMed
-
- J. Wu, Y. Wang, Z. Li, H. Miao, Accuracy of Fukuoka and American gastroenterological association guidelines for predicting advanced neoplasia in pancreatic cyst neoplasm: A meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 26, 4522–4536 (2019). - PubMed
-
- M. Tanaka, C. Fernández-del Castillo, T. Kamisawa, J. Y. Jang, P. Levy, T. Ohtsuka, R. Salvia, Y. Shimizu, M. Tada, C. L. Wolfgang, Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 17, 738–753 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

