Individual phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins have distinct functions that do not involve lipid transfer activity
- PMID: 36930803
- PMCID: PMC10424146
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008735
Individual phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins have distinct functions that do not involve lipid transfer activity
Abstract
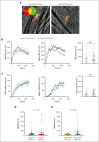
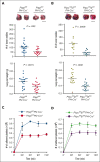
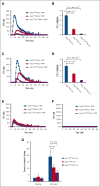
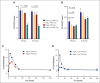
Platelets use signal transduction pathways facilitated by class I phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins (PITPs). The 2 mammalian class I PITPs, PITPα and PITPβ, are single PITP domain soluble proteins that are encoded by different genes and share 77% sequence identity, although their individual roles in mammalian biology remain uncharacterized. These proteins are believed to shuttle phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine between separate intracellular membrane compartments, thereby regulating phosphoinositide synthesis and second messenger formation. Previously, we observed that platelet-specific deletion of PITPα, the predominantly expressed murine PITP isoform, had no effect on hemostasis but impaired tumor metastasis formation and disrupted phosphoinositide signaling. Here, we found that mice lacking the less expressed PITPβ in their platelets exhibited a similar phenotype. However, in contrast to PITPα-null platelet lysates, which have impaired lipid transfer activity, PITPβ-null platelet lysates have essentially normal lipid transfer activity, although both isoforms contribute to phosphoinositide synthesis in vitro. Moreover, we found that platelet-specific deletion of both PITPs led to ex vivo platelet aggregation/secretion and spreading defects, impaired tail bleeding, and profound tumor dissemination. Our study also demonstrated that PITP isoforms are required to maintain endogenous phosphoinositide PtdInsP2 levels and agonist-stimulated second messenger formation. The data shown here demonstrate that the 2 isoforms are functionally overlapping and that a single isoform is able to maintain the homeostasis of platelets. However, both class I PITP isoforms contribute to phosphoinositide signaling in platelets through distinct biochemical mechanisms or different subcellular domains.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation of S.H.M is Department of Internal Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan.
Figures




References
-
- Cockcroft S. The diverse functions of phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;362:185–208. - PubMed
-
- Yoder MD, Thomas LM, Tremblay JM, Oliver RL, Yarbrough LR, Helmkamp GM., Jr. Structure of a multifunctional protein. Mammalian phosphatidylinositol transfer protein complexed with phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(12):9246–9252. - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft S, Carvou N. Biochemical and biological functions of class I phosphatidylinositol transfer proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1771(6):677–691. - PubMed
-
- Morgan CP, Allen-Baume V, Radulovic M, Li M, Skippen A, Cockcroft S. Differential expression of a C-terminal splice variant of phosphatidylinositol transfer protein beta lacking the constitutive-phosphorylated Ser262 that localizes to the Golgi compartment. Biochem J. 2006;398(3):411–421. - PMC - PubMed

