Low contralateral neck recurrence risk with ipsilateral neck radiotherapy in N2b tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36931141
- PMCID: PMC10400120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2023.106362
Low contralateral neck recurrence risk with ipsilateral neck radiotherapy in N2b tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: To characterize factors including nodal burden, pre-treatment imaging, and other patient factors which may influence the role of ipsilateral neck radiotherapy (IRT) in tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) with multiple involved ipsilateral nodes.
Methods: Patients with cT1-2N0-2bM0 (AJCC 7th edition) tonsillar SCC treated with definitive radiation therapy (RT) at Duke University Medical Center from 1/1/1990-10/1/2019 were identified. Patient, tumor, and treatment characteristics were compared between those that received bilateral neck RT (BRT) versus IRT. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was estimated with Kaplan-Meier method. A subset analysis of patients with N2b disease was performed. Patterns of recurrence were analyzed.
Results: 120 patients with cT1-2N0-2b tonsillar SCC were identified, including 71 with N2b disease (BRT: n = 30; IRT: n = 41). Median follow-up was 80 months (range: 7-209). No N2b patients who received IRT had > 1 cm of soft palate/base of tongue extension. N2b patients treated with IRT had a median of 3 (range 2-9) involved lymph nodes, with median largest nodal dimension of 2.8 cm (range 1.3-4.8 cm). 93 % of N2b patients who received IRT had staging by PET/CT, and 100 % received IMRT. For N2b patients treated with IRT, there were no contralateral neck recurrences, and 10 year RFS was 95 % (95 % CI 82 %-98 %).
Conclusions: For patients treated with IRT for well-lateralized N2b tonsillar SCC, we observed high rates of local control with no observed contralateral neck recurrence. These data suggest that BRT is not universally necessary for patients with multiple involved ipsilateral nodes, particularly in the setting of baseline staging with PET/CT.
Keywords: Ipsilateral neck radiation; Multiple ipsilateral nodes; N2b; Radiation; Tonsil cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
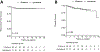

References
-
- Huang SH, Waldron J, Bratman SV, et al. Re-evaluation of ipsilateral radiation for T1–T2N0-N2b tonsil carcinoma at the princess Margaret hospital in the human papillomavirus era, 25 years later. Int J Radiat Oncol* Biol* Phys 2017;98(1): 159–69. - PubMed
-
- Biau J, Lapeyre M, Troussier I, et al. Selection of lymph node target volumes for definitive head and neck radiation therapy: a 2019 update. Radiother Oncol 2019; 134:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Yeung AR, Garg MK, Lawson J, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® ipsilateral radiation for squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil. Head Neck 2012;34(5):613–6. - PubMed
-
- Lynch J, Lal P, Schick U, et al. Multiple cervical lymph node involvement and extra-capsular extension predict for contralateral nodal recurrence after ipsilateral radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil. Oral Oncol 2014;50(9): 901–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

