Serpin B9 controls tumor cell killing by CAR T cells
- PMID: 36931661
- PMCID: PMC10030924
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2022-006364
Serpin B9 controls tumor cell killing by CAR T cells
Abstract
Background: Initial clinical responses with gene engineered chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in cancer patients are highly encouraging; however, primary resistance and also relapse may prevent durable remission in a substantial part of the patients. One of the underlying causes is the resistance mechanisms in cancer cells that limit effective killing by CAR T cells. CAR T cells exert their cytotoxic function through secretion of granzymes and perforin. Inhibition of granzyme B (GrB) can underlie resistance to T cell-mediated killing, and it has been shown that serine proteinase inhibitor serpin B9 can effectively inhibit GrB. We aimed to determine whether expression of serpin B9 by cancer cells can lead to resistance toward CAR T cells.
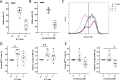
Methods: Serpin B9 gene and protein expression were examined by R2 or DepMap database mining and by western blot or flow cytometric analysis, respectively. Coculture killing experiments were performed with melanoma cell line MeWo, diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell line OCI-Ly7 or primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells as target cells and natural killer cell line YT-Indy, CD20 CAR T cells or CD19 CAR T cells as effector cells and analyzed by flow cytometry.
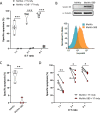
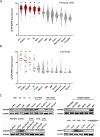
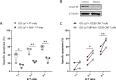
Results: Serpin B9 protein expression was previously shown to be associated with clinical outcome in melanoma patients and in line with these observations we demonstrate that enforced serpin B9 expression in melanoma cells reduces sensitivity to GrB-mediated killing. Next, we examined serpin B9 expression in a wide array of primary tumor tissues and human cell lines to find that serpin B9 is uniformly expressed in B-cell lymphomas and most prominently in DLBCL and CLL. Subsequently, using small interfering RNA, we silenced serpin B9 expression in DLBCL cells, which increased their sensitivity to CD20 CAR T cell-mediated killing. In addition, we showed that co-ulture of primary CLL cells with CD20 CAR T cells results in selection of serpin B9-high CLL cells, suggesting these cells resist CAR T-cell killing.
Conclusions: Overall, the data indicate that serpin B9 is a resistance mediator for CAR T cell-mediated tumor cell killing that should be inhibited or bypassed to improve CAR T-cell responses.
Keywords: Cytotoxicity, Immunologic; Hematologic Neoplasms; Immunotherapy, Adoptive.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: VP received royalty payments related to venetoclax. VP, ZS, and TK are inventors on a patent for improving cytotoxicity of gene engineered T and NK cells. MCM received honoraria from Medscape, Jansen Cilag, and BMS. ZS and JK are inventors on different patents for γδ T -cell receptor sequences, recognition mechanisms, and isolation strategies. JK is scientific cofounder and shareholder of Gadeta. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shadman M, Gopal AK, Smith SD, et al. . CD20 targeted CAR-T for high-risk B-cell non-hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 2019;134(Supplement_1):3235. 10.1182/blood-2019-125102 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
