Amide-to-ester substitution as a stable alternative to N-methylation for increasing membrane permeability in cyclic peptides
- PMID: 36932083
- PMCID: PMC10023679
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36978-z
Amide-to-ester substitution as a stable alternative to N-methylation for increasing membrane permeability in cyclic peptides
Abstract
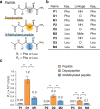
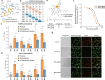
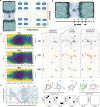
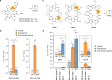
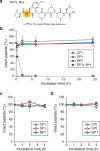
Naturally occurring peptides with high membrane permeability often have ester bonds on their backbones. However, the impact of amide-to-ester substitutions on the membrane permeability of peptides has not been directly evaluated. Here we report the effect of amide-to-ester substitutions on the membrane permeability and conformational ensemble of cyclic peptides related to membrane permeation. Amide-to-ester substitutions are shown to improve the membrane permeability of dipeptides and a model cyclic hexapeptide. NMR-based conformational analysis and enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations suggest that the conformational transition of the cyclic hexapeptide upon membrane permeation is differently influenced by an amide-to-ester substitution and an amide N-methylation. The effect of amide-to-ester substitution on membrane permeability of other cyclic hexapeptides, cyclic octapeptides, and a cyclic nonapeptide is also investigated to examine the scope of the substitution. Appropriate utilization of amide-to-ester substitution based on our results will facilitate the development of membrane-permeable peptides.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures