Exosome-derived circCCAR1 promotes CD8 + T-cell dysfunction and anti-PD1 resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36932387
- PMCID: PMC10024440
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-023-01759-1
Exosome-derived circCCAR1 promotes CD8 + T-cell dysfunction and anti-PD1 resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) can be encapsulated into exosomes to participate in intercellular communication, affecting the malignant progression of a variety of tumors. Dysfunction of CD8 + T cells is the main factor in immune escape from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Nevertheless, the effect of exosome-derived circRNAs on CD8 + T-cell dysfunction needs further exploration.
Methods: The effect of circCCAR1 on the tumorigenesis and metastasis of HCC was assessed by in vitro and in vivo functional experiments. The function of circCCAR1 in CD8 + T-cell dysfunction was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), western blotting and flow cytometry. Chromatin immunoprecipitation, biotinylated RNA pull-down, RNA immunoprecipitation, and MS2 pull-down assays were used to the exploration of mechanism. A mouse model with reconstituted human immune system components (huNSG mice) was constructed to explore the role of exosomal circCCAR1 in the resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in HCC.
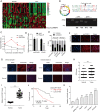
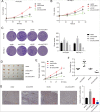
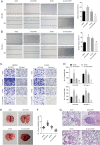
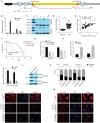
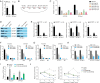
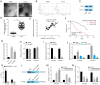
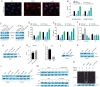
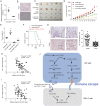
Results: Increased circCCAR1 levels existed in tumor tissues and exosomes in the plasma of HCC patients, in the culture supernatant and HCC cells. CircCCAR1 accelerated the growth and metastasis of HCC in vitro and in vivo. E1A binding protein p300 (EP300) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A3 (EIF4A3) promoted the biogenesis of circCCAR1, and Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP)-mediated m6A modification enhanced circCCAR1 stability by binding insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3). CircCCAR1 acted as a sponge for miR-127-5p to upregulate its target WTAP and a feedback loop comprising circCCAR1/miR-127-5p/WTAP axis was formed. CircCCAR1 is secreted by HCC cells in a heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNPA2B1)-dependent manner. Exosomal circCCAR1 was taken in by CD8 + T cells and caused dysfunction of CD8 + T cells by stabilizing the PD-1 protein. CircCCAR1 promoted resistance to anti-PD1 immunotherapy. Furthermore, increased cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator 1 (CCAR1) induced by EP300 promoted the binding of CCAR1 and β-catenin protein, which further enhanced the transcription of PD-L1.
Conclusions: The circCCAR1/miR-127-5p/WTAP feedback loop enhances the growth and metastasis of HCC. Exosomal circCCAR1 released by HCC cells contributes to immunosuppression by facilitating CD8 + T-cell dysfunction in HCC. CircCCAR1 induces resistance to anti-PD1 immunotherapy, providing a potential therapeutic strategy for HCC patients.
Keywords: Anti-PD1; CCAR1; Exosome; Hepatocellular carcinoma; circRNA.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, Al-Raddadi R, Alvis-Guzman N, Amoako Y, Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer C et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1683–1691. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Khoueiry AB, Sangro B, Yau T, Crocenzi TS, Kudo M, Hsu C, Kim TY, Choo SP, Trojan J, Welling THR, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2492–2502. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31046-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D, Verslype C, Zagonel V, Fartoux L, Vogel A, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:940–952. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

