Characterization of leaf surface phenotypes based on light interaction
- PMID: 36932424
- PMCID: PMC10024457
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-023-01004-2
Characterization of leaf surface phenotypes based on light interaction
Abstract
Background: Leaf surface phenotypes can indicate plant health and relate to a plant's adaptations to environmental stresses. Identifying these phenotypes using non-invasive techniques can assist in high-throughput phenotyping and can improve decision making in plant breeding. Identification of these surface phenotypes can also assist in stress identification. Incorporating surface phenotypes into leaf optical modelling can lead to improved biochemical parameter retrieval and species identification.
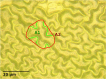
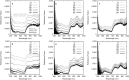
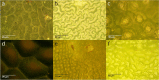
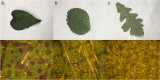
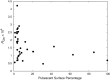
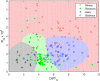
Results: In this paper, leaf surface phenotypes are characterized for 349 leaf samples based on polarized light reflectance measured at Brewster's Angle, and microscopic observation. Four main leaf surface phenotypes (glossy wax, glaucous wax, high trichome density, and glabrous) were identified for the leaf samples. The microscopic and visual observations of the phenotypes were used as ground truth for comparison with the spectral classification. In addition to surface classification, the microscope images were used to assess cell size, shape, and cell cap aspect ratios; these surface attributes were not found to correlate significantly with spectral measurements obtained in this study. Using a quadratic discriminant analysis function, a series of 10,000 classifications were run with the data randomly split between training and testing datasets, with 150 and 199 samples, respectively. The average correct classification rate was 72.9% with a worst-case classification of 60.3%.
Conclusions: Leaf surface phenotypes were successfully correlated with spectral measurements that can be obtained remotely. Remote identification of these surface phenotypes will improve leaf optical modelling and biochemical parameter estimations. Phenotyping of leaf surfaces can inform plant breeding decisions and assist with plant health monitoring.
Keywords: Leaves; Light; Polarization; Pubescence; Reflectance; Surface roughness; Wax.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Gausman HW, Allen WA, Cardenas R. Reflectance of cotton leaves and their structure. Remote Sens Environ. 1969;1(1):19–22. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(69)90055-8. - DOI
-
- Jacquemoud S, Baret F. PROSPECT: a model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote Sens Environ. 1990;34(2):75–91. doi: 10.1016/0034-4257(90)90100-Z. - DOI
-
- Féret JB, François C, Asner GP, Gitelson AA, Martin RE, Bidel LP, et al. PROSPECT-4 and 5: advances in the leaf optical properties model separating photosynthetic pigments. Remote Sens Environ. 2008;112(6):3030–3043. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.02.012. - DOI
-
- Féret JB, Gitelson AA, Noble SD, Jacquemoud S. PROSPECT-D: towards modeling leaf optical properties through a complete lifecycle. Remote Sens Environ. 2017;193:204–215. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.03.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

