The Fat Kidney
- PMID: 36933154
- PMCID: PMC10250266
- DOI: 10.1007/s13679-023-00500-9
The Fat Kidney
Abstract
Purpose of review: The purpose of this review is to summarize the current evidence on the role of obesity in the development and progression of chronic kidney disease and the current evidence on nutritional, pharmacological, and surgical strategies for the management of individuals with obesity and chronic kidney disease.
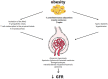
Recent findings: Obesity can hurt the kidney via direct pathways, through the production of pro-inflammatory adipocytokines, and indirectly due to systemic complications of obesity, including type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. In particular, obesity can damage the kidney through alterations in renal hemodynamics resulting in glomerular hyperfiltration, proteinuria and, finally, impairment in glomerular filtratation rate. Several strategies are available for weight loss and maintenance, such as the modification of lifestyle (diet and physical activity), anti-obesity drugs, and surgery therapy, but there are no clinical practice guidelines to manage subjects with obesity and chronic kidney disease. Obesity is an independent risk factor for the progression of chronic kidney disease. In subjects with obesity, weight loss can slow down the progression of renal failure with a significant reduction in proteinuria and improvement in glomerular filtratation rate. Specifically, in the management of subjects with obesity and chronic renal disease, it has been shown that bariatric surgery can prevent the decline in renal function, while further clinical studies are needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety on the kidney of weight reducing agents and the very low-calorie ketogenic diet.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Diet; Hyperfiltration; Obesity; Tirzepatide.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH. WHO European regional obesity report 2022 [Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/353747].
-
- Stevens PE, Levin A, Kidney disease: improving global outcomes chronic kidney disease guideline development work group M. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: synopsis of the kidney disease: improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158(11):825–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

